The purpose of this work is to study and analyze issues related to management practices at hotel-type enterprises.
The object of research in this course work is a hotel and its organization structure".
In this course work, the following issues will be considered:
- structure of management of hotels, types of organizational structures;
- characteristics of the organizational and economic activity of the researched object;
- analysis of its organizational and legal form;
- analysis of the structure of the management apparatus;
- economic indicators of economic activity;
- analysis of the basic services of the hotel
CHAPTER 1.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
1.1 Governance structure for hospitality industry enterprises
Hotels and restaurants are not only the most important type of enterprises of economic activity, but also a complex organizational structure characterized by the distribution of goals and tasks of management between whole departments and individual employees.
Organizational structure of management - is the aggregate of management links that are in a strict subordination and provide the interrelationship between the control and managed systems.
The organizational structure of management consists of the composition, correlation, location and interconnection of the individual subsystems of the organization. Creation of such structure is directed, first of all, on distribution between the separate divisions of the organization of the rights and responsibility.
The following elements are distinguished in the structure of hotel management: links (departments), levels (steps) of management and communication - horizontal and vertical.
The management units include structural units, as well as individual specialists who perform the relevant management functions or a part of them (for example, managers who regulate and coordinate the activities of several structural divisions).
At the center of the formation of a management unit is the department's performance of a specific management function. Established between the communication departments that are horizontal.
The level of management - is the totality of management links that occupy a certain stage in the management system of the hotel. The management stages are in vertical dependence and obey each other: managers of a higher stage of management make decisions that are specified and brought to the lower levels.
Changing the priorities of entrepreneurial activity (business operation) - from the acquisition of business (in the 50s) to the adoption of the theory of the social contract (the business owes its existence to society and must be responsible not only to its shareholders but also to the community) - has led to a change in principles (Table 1.), which directly affected the work with the staff.
Table 1. Principles of functioning of the production of LLC "SPSZ"
| TRADITIONAL PRINCIPLES | MODERN PRINCIPLES |
| Individualistic ethics, property law, independent solutions | Development of social ethics with emphasis on local society, collective participation and responsibility, |
| social and cultural impact on personal well-being | |
| Personal benefits and prosperity of each - a pledge of a higher social welfare | Necessity of concerted public action |
| The rise of efficiency through the division of labor and specialization | Awareness of the limit of specialization from positions |
| human satisfaction | |
| Enterprise as an economic entity | Organization of an enterprise as a socio-economic system |
| Profit Maximization as the Only Goal | Profit is the main goal, but awareness of social goals is growing. Multipurpose satisfaction |
| Universal emphasis on profitable and effective economic achievements | Focus on the profitability, effectiveness and satisfaction of participants |
| Organization of the enterprise as a closed system | Organization of an enterprise as an open system that interacts with the environment |
| Reaction only to the market and competitive environment. | Reaction to many interested groups and social forces |
| Approach to government activities from the perspective of the government | Understanding the role of government in accordance with public goals |
| Man strives to use nature and dominate it. | Life in harmony with nature and subordination to it |
| Strong linkage between the use of environmental resources and economic growth | Awareness of the limits of growth and actions for preserving environmental integrity |
| Unlimited use of science and technology. | Awareness of the limit of science and technology. Recognition of the need to control the applied use of technology |
| A View of Science from the Point of View of Non-Intervention and Determinism | |
| Reduction of public expectations from the enterprise to the production of material values and services | Society expects the enterprise to address the problems of the quality of life in a broader sense |
| Measurement of the enterprise's achievements in profit. | Enterprise valuation by profit and social performance indicators |
An important feature of the company's internal management at OOO SPSZ is the unified and comprehensive impact on the entire staff as a whole. In this regard, there is a system of personnel work, which:
1) integrates the management of personnel into the overall management system of the firm, links it to strategic attitudes and corporate culture, as well as production, marketing, quality improvement, etc .;
2) includes an extensive system of permanent and programmatic measures for regulating employment, planning workplaces, organizing selection, placement and training of personnel, forecasting the content of work;
3) involves careful consideration (including in information systems) of the qualities and professional characteristics of employees, as well as the results of their activities;
4) provides for propaganda and educational work with employees of the company and with members of their families (Japanese practice);
5) centralizes the management of labor in the firm in the hands of one of its leaders, and also carries out measures to improve the mechanism of personnel work.
The essence of HR management at LLC SPPS is that people - are competitive wealth of the company, which should be placed, developed, motivated along with other resources to achieve its strategic goals.
1.2 Types of organizational structures
Firstly, let us clarify one important thing - what do we mean by the structure of the enterprise. We have in mind the organizational structure, in the form of a schematic representation of the various structural units of the enterprise that exist in the company. It also includes an organizational structure or scheme (abbreviated to an organizational chart) that organizes and tidies up all business processes of the enterprise, determines relationships and zones of responsibility. It also shows the way to obtain the final result of the activity.
We will not consider schematic representations of organizational structures, since there are many variants of these schemes. In small companies with the size of up to 50 employees, usually the majority of the schemes are closed on the CEO. If you want to test this, then conduct a survey among your employees on the topic "Who is your immediate supervisor" or "To whom are you applying for the approval of your actions and decisions" and you will see where all the problems of the company flock.
We will focus on the types of organizational structures of the enterprise that carry, at least some sense and sum up, which one is the most optimal for business development.
So, types of organizational structures:
In the management practice of the hospitality industry, the following types of organizational structures are most common:
• Linear;
• Functional;
• linear-functional.
Linear organizational structure of management. Linear relations in the hotel reflect the movement of managerial decisions and information emanating from the so-called line manager, that is, a person fully responsible for the activities of the hotel (usually small) or its structural units (large). This is one of the simplest organizational management structures.
It is characterized by the fact that at the head of each structural unit there is a leader with all the powers that exercise all management functions (Figure 1).
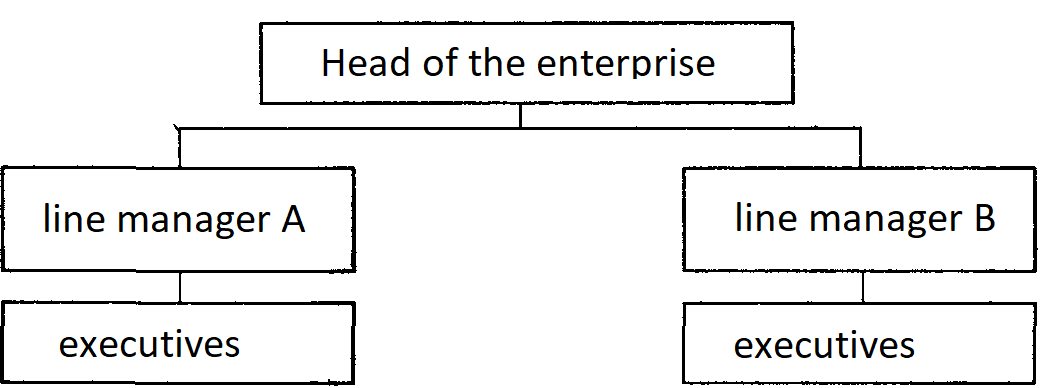
Fig. 1. The linear structure of organization management
Источник: [http://tourlib.net/books_tourism/lojko9-3.htm]
As you can see from Figure 2.1, with linear control, each link and each subordinate has one supervisor, where which all the control commands pass through one channel.
In this case, the management units are responsible "for the results of all the activities of the objects they manage.
We are talking about the subject selection of managers, each of which performs all kinds of work and makes decisions related to the management of this object.
Functional organizational structure of management. Functional management is carried out by a certain set of units specialized in performing specific types of work necessary for making decisions in the system of linear control (Figure 2).
The idea is that the execution of certain functions is entrusted to specialists.
In the organization, as a rule, specialists of the same profile are merged into structural divisions (departments), for example, marketing department, reception department, planning department, etc.
Thus, the overall task of managing an organization is divided, starting with the average level, according to a functional criterion. Hence the name - the functional structure of management.
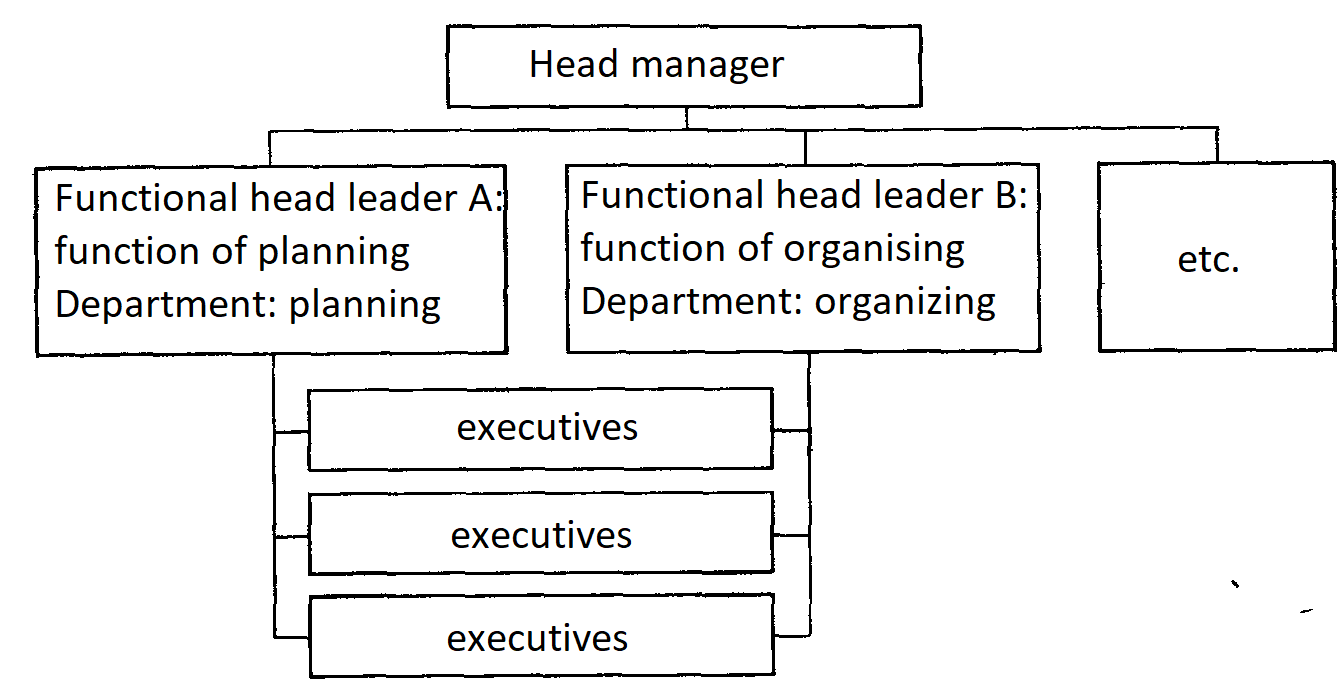
Fig. 2. Functional structure of organization management
Источник; [http://tourlib.net/books_tourism/zorin09.htm]
Functional management exists along with a linear one, which creates a double subordination for the performers.
As can be seen in Figure 2, instead of universal managers (Figure 1), who must understand and perform all management functions, a staff of specialists with high competence in their field and responsible for a certain direction (for example, planning and forecasting) appears.
This functional specialization of the management apparatus significantly increases the effectiveness of the hotel.
Like the linear, functional structure has its advantages and disadvantages.
Linear-functional (staff) structure of hotel management. With this management structure, the entire line of power is assumed by the line manager, who heads a certain team.
While development of specific issues and preparing appropriate decisions, programs, plans, it is assisted by a special apparatus consisting of functional units (offices, departments, bureaus, etc.) (Fig. 3).
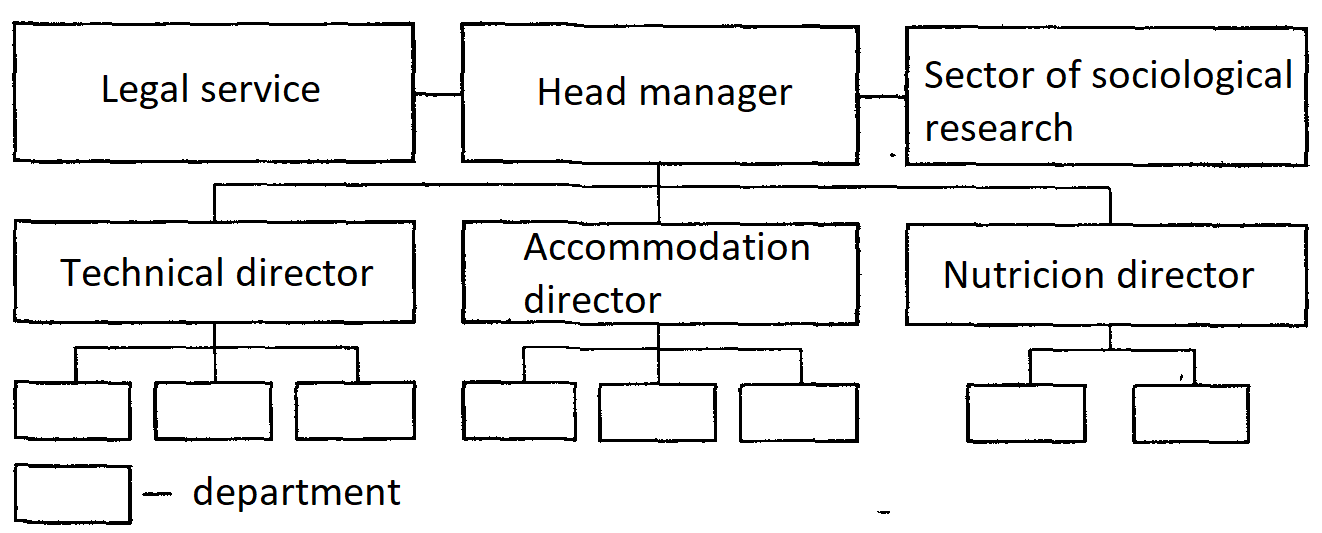
Fig. 3. The linear-functional management
Источник: [http://sport.bobrodobro.ru/3044]
Thus, the linear-functional structure includes special units with line managers.
It also has its positive moments and disadvantages.
The organizational structure of the hotel company is determined by its purpose, the capacity of the hotel stock, the specifics of the guests and a number of other factors.
CHAPTER 2
FORMATION AND CONSTRUCTION OF HIERARCHY OF SUBORDINATION
2.1 Hierarchy of subordination in hotel
A little theoretical explanation first. The subordination scheme, as a rule, is a pyramid, i.e. consists of several levels of the hierarchy. At the top level - the head of the organization, who directly subordinates the leaders of a lower level. The latter, in turn, also have direct subordination to lower-level workers, and so on.
The hierarchy of subordination is built on the division of labor. In this case, you can distinguish between vertical and horizontal separation.
Vertical differentiation is related to the division into levels of power built in a hierarchical order. The power is distributed according to the posts in accordance with the level in the hierarchy: the head of the upper level manages the activities of the lower levels, i. in a formal sense has more power and status.
Functions of managers of different levels differ from each other. Thus, the most important tasks of the managers of the lower level are to coordinate the work of the performers and directly manage other resources, including equipment and materials. Mid-level managers are often the main "internal" managers in business, because they usually spend 75% of their time doing operational management. They focus on coordinating the work of groups led by lower-level managers. In large firms, there are often several levels of middle managers. Senior managers are responsible for the activities of the firm as a whole. Their time is divided between strategic planning, management and control of the activities of the company's main divisions, taking into account the requirements for the firm of various external entities, for example consumers
Horizontal differentiation reflects the division of spheres of management in directions requiring specialized knowledge and skills.
The horizontal distribution of spheres of management is called the departmentalization and is associated with the grouping of the company's employees into specialized divisions that carry out certain types of activities.
Here’s a typical pyramidal structure of hotel management is presented in Fig.
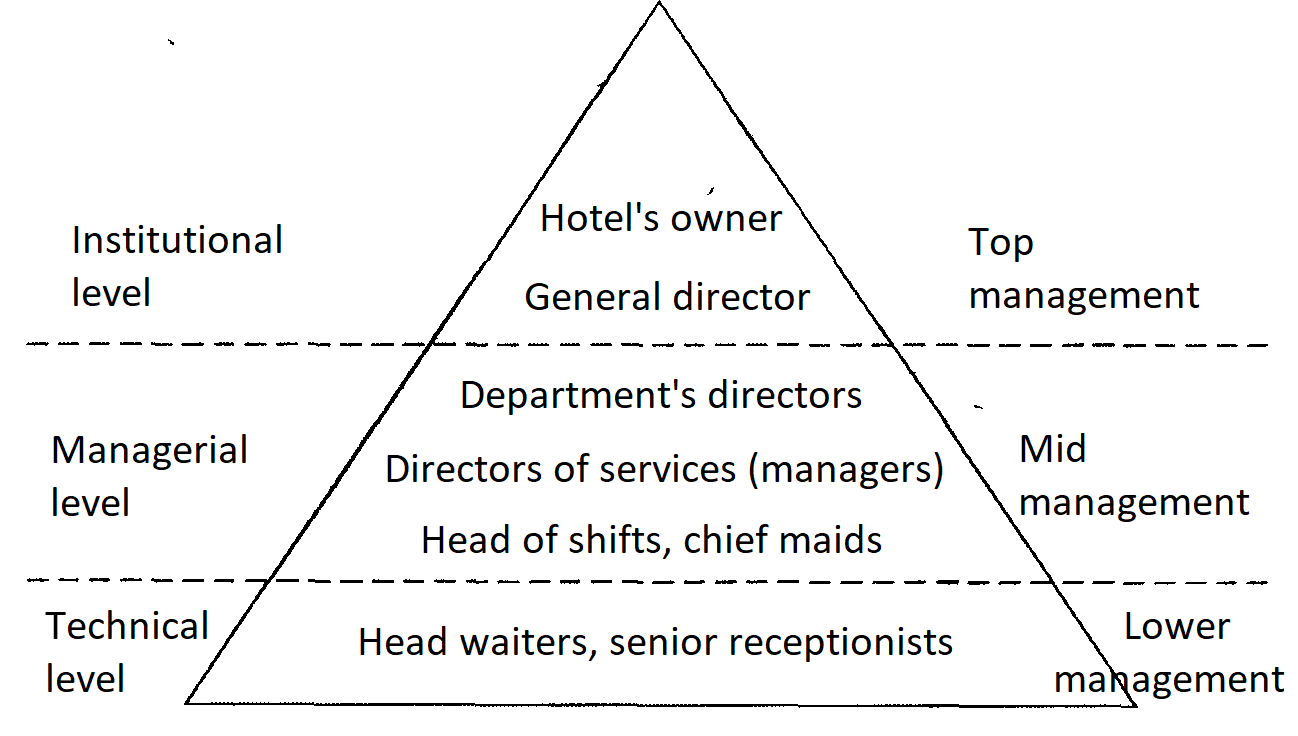
Fig. 4. Typical pyramidal structure of hotel management
Источник: [https://studfiles.net/preview/5992155/page:26/]
The hotel owner and the general director who make general strategic decisions represent the highest level of management of the hotel enterprise.
In this case, the owner can be an individual or an entire corporation.
An example of the strategic goal of a hotel company, which is determined by the owner, can be the orientation of the enterprise to serve a certain segment of the market: group of tourists or individual tourists, tourists who seek for rest and health restoration, or participants in congresses and conferences, etc.
In the development of the strategic goal, the owner can also make a decision that the restaurant, which is part of the hotel complex, will provide food only to its guests.
Another example, stemming from the main objective of the enterprise, can be the establishment of a certain level of prices for hotel accommodation.
Such solutions and tasks belong to the category of general, on which the size of the enterprise and the choice of location for its construction, architecture and interior, furniture, equipment, personnel selection depend on.
2.2 The organizing scheme of seven units of L. Ron Hubbard.
The first model of this organizational structure was developed by Hubbard in 1965, basically unchanged until today. For almost thirty years, it was subjected to verification and minor improvements. The basis of this structure is the business processes necessary for the enterprise to develop. The stages of these business processes are reflected in the structure. The universality of this structure is that it is suitable for both a small company and a multi-thousand corporation. When the enterprise develops, the basic model of the structure does not change, it only lengthens deeper into the divisions, without violating the natural business processes of the enterprise, and does not require emergency measures for restructuring. This model of structure can be imposed on any kind of activity. the main thing is to correctly prescribe all the business processes that are individual for each business, and write them into this model. The key point of this model is that the direct subordinates of the head of any level, there can be no more than five people. For each stage of business processes, its own unit is responsible (there are seven of them). There are separate committees consisting of heads of departments that coordinate and coordinate business processes at each stage, among themselves, plan and propose actions for the development and improvement of the enterprise's activity to the top management, the work of the committees is carried out on a weekly schedule, and on the remaining days, their functions as leaders. This allows you to quickly respond to emerging changes and keep the relationship between ordinary employees and the top management of the enterprise. Also, the basis of the foundations of this organizational structure is that the business processes of the enterprise smoothly pass from one unit to another and end with the end result of the whole enterprise. This allows you to identify, correct and prevent errors before a disaster occurs.
Advantages of the organizational chart of seven divisions:
1. The structure is lively and quickly reacting to changes in internal and external factors hindering the development of the enterprise;
2. Expansion of the enterprise does not require a global restructuring;
3. managers are freed from routine work and are engaged in a development strategy, while keeping their hands on the organization's pulse, and do not break away from the collective;
4. mutual responsibility of the units for the final result of the enterprise;
5. complete absence of duplicate functions and unnecessary, unnecessary work and fuss;
6. Timely detection and correction of errors at different stages of product production, which, of course, leads to a continuous improvement in quality;
7. In general, this model includes almost all the advantages of the previous structures;
Disadvantages of the organizational chart of seven divisions:
1. A disadvantage is one - you need to correctly write down all the business processes of an enterprise that are necessary for it to live and develop;
Conclusion: The most worthy structure of the enterprise. In support of this, the huge scope of this structure is applied to more than 140,000 enterprises around the world, including Russia.
CHAPTER 3.
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE OF THE HOTEL
3.1 Basic services of the hotel
To implement the closed technological cycle of customer service (Fig. 8) the following main services are provided in the hotel:
• Reservation;
• maintenance;
• reception and calculation part;
• room operation service.
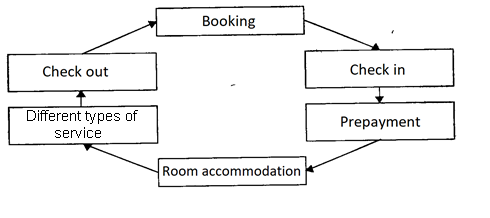
Fig. 5.
Technological cycle of customer service
Источник: [http://prohotelia.com/]
This is the minimum set of services that provide the provision of basic hotel service cycle.
At hotel enterprises of various types and different capacities, the number of services may be more or less than those listed above. Their functions may also vary. For example, only in the structure of large hotel complexes booking and service are independent structural units. In small and medium-sized enterprises, individual reception and placement personnel perform individual booking and customer service functions. This also applies to the service of marketing, engineering and operation, financial and accounting, commercial services.
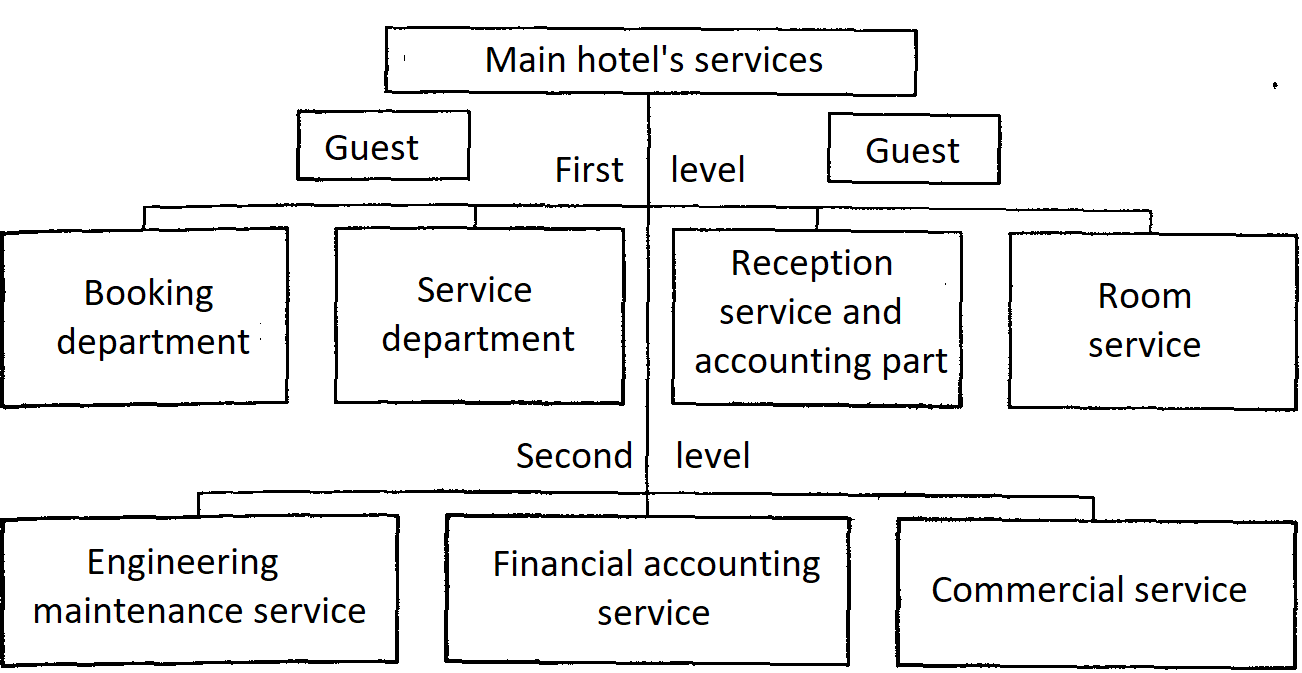
Fig.6. Basic hotel services
As shown in Figure 9, the hotel services, depending on the presence of contact with the guest are located on two levels. At the first level - services whose staff has direct contact with the guest (contact services), at the second level - services whose staff practically does not contact the guest (non-contact services). In the hotel industry, such a delineation of services is very important, as it affects the requirements for staff. So, the most important requirements for the personnel of contact services are the following:
• neat and attractive appearance (appropriate hairstyle, manicure, make-up, clothing, jewelry, etc.);
• impeccable behavior;
• knowledge of ethics and psychology of communication;
• communication skills;
• Foreign language skills;
• restriction of age (for example, for the receptionist for admission – age is up to 30 years).
Among the specialists in the field of hotel and restaurant management, the classification of the personnel of contact services is popular, which includes the following types:
1) "frozen" - personnel who are slow to respond to requests from guests, who do not show any personal initiative to help guests with something, very rarely smiling;
2) "gastrofactory" - the personnel creating the service by type of conveyor, when the opinion of the guests is not taken into account at all;
3) "friendly chaos" - doing nothing in essence, but at the same time having polite and smiling staff;
4) personnel providing service with high quality.
The most important requirements for the personnel of non-contact services are the availability of special education and work experience in this area.
Reservation service.
The functions of the reservation service include:
1. Reception of applications and their processing.
2. Drawing up the necessary documentation: the schedules of arrival for each day (week, month, quarter, year), maps of movement of the room fund.
The system of reservation of seats available must be carefully thought out and regulated. If the hotel is unable to fulfill its obligations under the accepted orders, it runs the risk of losing customers whose booking has not been completed, as well as terminating business relations with travel companies.
The opinion of some managers boils down to the fact that it is better to leave the numbers unoccupied than to not then execute the order. As a rule, these managers restrict booking only by availability. However, they often find themselves in a situation where the numbers remain unoccupied. The facts show that about 20% of guests who made a non-guaranteed reservation and about 5% who made a guaranteed order will not use their booking.
Customer Service:
From the point of view of the guests, the service department is the most important in the hotel, since the staff of this service works with customers in constant contact and performs all the functions related to their direct service.
Due to the importance of the first impressions of the customers about the hotel, the service personnel have a special responsibility. As a rule, the first guests are met by doormen who stand at the entrance to the hotel. They should greet the guests, help them get out of the car. The porter must have information about the services available in the hotel, about hotel events (conferences, banquets), about the place
The concierge provides many important services. They can be seen at a special table in the lobby of the hotel or directly on the floors. Until a certain time, the concierges were not hotel employees. They were independent entrepreneurs who bought the right to provide services to hotel customers. The most typical services provided by concierges include:
• purchase and delivery of tickets to theaters;
• reservation of a table in city restaurants;
• ordering and delivery of air, railway, bus tickets, information on the work of international, intercity and inland transport;
• reservation of places in the hairdresser, beauty salon, a doctor;
• information about local sights, museums, exhibitions, shops;
• Assistance in case of emergency (for example, calling a doctor, lawyer, notary);
• Execution of strictly personal clients' orders (purchases, visa processing, etc.). The importance of the functions performed by the concierge is evidenced by the creation of a professional concierge organization, the UPPGH (commonly referred to as the Clefs d'Or) ("golden keys" - crossed golden keys are the emblem that concierges wear in the buttonholes of uniforms.) . This organization includes about 4000 members from 24 countries.
Reception service and payment part
The reception service is often called the "heart" or "nervous center" of the hotel. With this service the guest contacts most of all, here he applies for information and services during his stay in the hotel.
The most important functions of the reception service include welcoming the guest and performing the necessary formalities when arranging it. The receptionist (porter) is usually located after the doorman at the entrance, practically the first employee of the hotel, with whom the guest contacts. The first, often the strongest impression of the hotel depends on how the guest is greeted, how good he will be greeted, how quickly the necessary formalities will be carried out (checking the reservation, filling in the application form, prepayment). In this connection, the following requirements are imposed on the reception service:
• The reception should be located in the immediate vicinity of the entrance to the hotel. In the case of a large area of the hotel lobby, the dynamic character of the interior should orient the visitor towards the location of the reception desk;
• The reception desk should be clean, it should not have randomly scattered papers and unnecessary items on it;
• the reception staff must have an impeccable appearance and act accordingly. Guests need to talk only while standing. You must not force the guests to wait and should always remember that there is no more important work than the reception of guests.
In reception service there is also a shield for keys from numbers. As a rule, it is equipped with special cells for correspondence of guests, telephone messages and other written information.
Immediately after placing the guest at the hotel, the settlement part opens an account in his name. Usually the guest uses various hotel services, presenting a business card or calling the room number. These services provide information about the expenses of the guest in the calculation part, which includes them in the common account. At the end of the guest's stay, the calculated part is matched with him and informs all hotel services about it. One of the functions of the reception service is the keeping of the guest card. For each guest after his stay in the hotel, a special card is filled out, which contains information collected from all the services of the hotel that had contact with the guest. This information enables the staff to significantly improve the quality of service, allows to anticipate the preferences and wishes of the guest. Such work is very important for the acquisition of regular customers and is an additional advertisement for the hotel. At modern hotel enterprises, this work is carried out using a computer program that allows you to create an extensive database of customers.
Room operation service.
The most important function of the operation of the room fund is to maintain the necessary level of comfort and sanitary and hygienic state of hotel rooms, as well as public facilities (halls, foyers, passageways, corridors)
By the number of employed personnel, this service is the largest service of the hotel. As a rule, up to 50% of all hotel employees work here.
Room manager is headed by another manager, who is subordinated to maids, floor attendants, supervisors, stewards and some other categories of employees.
Depending on the type of hotel, each maid cleans and tidies from 16 to 20 rooms a day (17 rooms - the norm for one maid in the US). According to the regulations of the Swiss Union of hotel owners for,there are 20 minutes to clean a room where a guest is still checked in. Cleaning of the released room - 30 minutes. In some hotels there is a replacement super-wiser, which monitors the work of changing the maid, in order to be completely sure that the premises are cleaned in accordance with the standards. It is also the responsibility of the supervisor to send information about free and occupied numbers to the reception service.
In hotels of high categories of service (luxury hotels) there are stewards, which begin their work in the afternoon. The duties of the stewards include providing each room with fresh towels, giving the room a smart look, and installing a retractable bed. This is a tradition for high-end hotels in America, which is strictly enforced.
2.2 Methods for optimizing the organizational structure
The goal is to increase the manageability and transparency of the business by consolidating the areas of responsibility and authority
The procedure for optimizing the organizational structure includes:
1. Express analysis of needs for counseling
2. Diagnostics of existing organizational structures (organizational, functional, information, personnel)
3. Formation of development strategy
4. Reorganization of business processes (lines of business)
5. Reorganization of key management functions
6. Reorganization of the company management structure
7. Training of personnel
8. Implementation of changes
Methods of work to optimize the organizational structure of the company:
1. Expert consultation (interview, analysis of documents, data collection)
2. Working sessions
Result:
1. Fixing areas of responsibility and authority
2. Clear distribution of management functions by organizational links
3. Fixing the place of each employee and division in the process of the company's activities
The topic of optimization of organizational structures, which was so popular a few years ago, now does not cause such a keen interest of managers. Until resent time, thinking of changes in the company, the directors first of all started to draw squares of the new structure. Very often the procedure resembled a simple permutation of the terms, from the change in the locations of which, as is known, the amount does not change. Today, managers have become more sophisticated in management theory, and, improving the organization, use other management tools, which can not be called a positive trend.
However, the topic of organizational construction of business, or organizational structures, continues to be relevant even if the reserves in this direction are still large. This article is based on the analysis of our practical experience in the field of diagnostics and optimization of organizational structures.
There are not many principles for constructing optimal structures, nevertheless, they are often violated.
Here are the main ones:
Correspondence of the type of organizational structure of the company, its type, size, industry.
Correspondence of the organization structure of its strategy.
Unity, the organization should not have two directors.
Compliance with the norm of controllability.
Relationship of the main business processes and structural units.
For one functional area there should be one unit, for one task - one post
Clear identification of who and who is subordinate and on what issues.
Correspondence of authority and responsibility.
Let's consider each principle in more detail.
Correspondence of the type of structure to the specifics of the company, its type, size, industry. There are several basic types of organizational structures that differ depending on how the organization is divided into divisions.
1. Simple structure.
There are no units, all employees obey the first person.
2. Linear-functional structure.
There are linear units for basic production (for example, workshops) and functional units depending on the function (for example, the department of the chief technologist, the marketing department, the accounting department, the department of labor and wages, etc.), which serve the line divisions.
3. The matrix structure.
There are functional units. Linear units are temporary and created for the implementation of the project. Each employee is subordinated to the project manager to carry out his part of the work in the project and functionally to the head of his department. For example, the project in the publishing house "Development of the concept of a new series." This project will include specialists from various fields: a financier, a marketer, a designer, an artist, etc. Each of them will follow the project manager for the implementation of this project, but for other tasks - his immediate supervisor. For example, a marketer will solve other problems in the marketing of the publishing house as a whole.
If the organization is large and some of it functions according to the principles of the matrix structure, and the part as a linear-functional structure, then they speak of a conglomerate structure.
4. Divisional structure.
This is the most common structure of holding companies. A headquarters is created, where the functional units that supervise the activities of the whole holding are concentrated (for example, finance, development, marketing, personnel). In addition, divisions are created (by product type, by customer group, by geographic region), which are practically independent organizations. The divisional structure is the development of a linear-functional structure. In this structure it is very important to choose which functions to provide to the headquarters, and which ones can be assigned to the division level. The choice of structure is influenced by the type of organization, namely its following characteristics:
company size
industry, the main business process
production cycle
objectives of the organization (commercial and non-commercial)
Quite often, companies choose the type of structure that does not match the type of organization.
Organizations of the third sector are generally better organized in a matrix type. They are on the one hand small, on the other hand, often do not have the ability to keep all employees in the state, it is more profitable for them to invite specialists to the task, the project. People who have devoted themselves to the development of the third sector, as a rule, are more freedom-loving, creative, socially-oriented. And stability and high incomes do not represent for them such value, as for people working in state and commercial organizations. Therefore, the matrix structure corresponds very well to the specifics of the third sector.
As we see, the linear-functional type of structure is the most common, and managers tend to use it regardless of the features of the organizations they lead. This is due to the familiarity of this type of structure. Many managers simply do not have experience working in other structures, and therefore their capabilities are also poorly represented.
Correspondence of the structure of the strategy.
It is important to understand the extent to which the established structure corresponds to the goals that the organization sets for itself. In addition, if there have been changes in the strategy, it is necessary to check whether the existing structure is capable of implementing a new strategy. If not, it must be changed urgently.
Unity, the organization should not have two directors.
The principle is obvious, however, even it is sometimes broken. We know a company that has two directors. Usually they are owners, formally they are directors of different organizations, but since these organizations are actually linked (for example, the production and trading companies) and the functions between the directors are not divided, it turns out that they are managed together. Naturally, this leads to various problems, for example: The same decision can be taken by one, and canceled by another director, as a result, the situation drags on and time is missed.
Employees can use this position and manipulate managers, solving questions with those of them who will rather agree and support the proposal. There are even options for bleeding directors, when, for example, employees may not perform the assignment, referring to the order of another director.
In case of failures, no one is responsible, everyone believes that the other is to blame.
Norm of controllability
The classical norm of controllability is 7 + 2. It is this number of people that can be managed efficiently. Naturally, this rule refers to top management, which manages employees engaged in fundamentally different types of activities and, accordingly, having different tasks and evaluation criteria. Heads of middle management can effectively manage a slightly larger number of employees, if some of them perform the same functions. A head of the lower level (for example, foreman) can lead well even more workers, especially if they all do the same job with the same evaluation criteria.
In fact, even if a complex structure is adopted in the company, the manager tries to manage it as simple, that is, to manage almost all the personnel. He obeys not only his deputies (directors of directions), but also their subordinates. In such conditions, the role of middle management is reduced, they do not have sufficient powers, they do not solve anything and become almost superfluous. On the other hand, the manager becomes more and more congested, does not have time, gets tired, misses important points and loses control. Strong excess of the norm of controllability suffer and large (former Soviet) enterprises. As a rule, at such enterprises the general director can have up to 15 deputies on various issues, as well as a dozen executives who also directly report to the director. Therefore, the first thing that is done at such enterprises during restructuring is to reduce the subordinates of the general director, creating a board of directors. Each member of this council is really the director of the direction: for production, for finance, for commerce, for personnel, etc. and bears full responsibility for his work. The task of the Director General is to coordinate the activities of all within the chosen strategy.
Relationship of the main business processes and structural units.
The structure should help to realize the main business process in the organization. If the main business process is divided between several departments and does not subordinate to a single center, then conflicts between departments are inevitable
For one functional area there should be one unit, for one task - one post
A violation of this principle results in such a common problem as duplication of functions or their "sagging". And both options are equally bad. If responsibility is borne by two people, then we can assume that no one carries it. There is always the opportunity to say that: "I thought it was his job." It's also bad if the function is not answered at all, that it is simply not provided for in the structure. Then this work is not done and the organization is missing some opportunities. By the extent to which the organization presents certain functions, you can even talk about its development.
The evolution of the development of organizational structures is as follows. At the 1st stage, the following functions are represented in the company: the unit responsible for the main production (technological) process; accounting; general management. This is the very first stage of development and organization and its structure.
At the 2nd stage, sales and purchases are allocated to a separate unit, these functions are derived from the main technological process and are separated. Then there are marketing, personnel, finance. And depending on the sequence in which these functions appear, one can speak about the preferences or knowledge of management. As a rule, managers start with what is closer and more understandable to them and what they see as an urgent necessity.
At the final stage of the formation of the structure of the organization, there are units responsible for development and investment, as well as corporate governance.
Clear identification of who and who is subordinate and on what issues.
It happens that employees themselves decide who they will obey, and who does not. This happens if the structure is spelled out insufficiently clearly or completely, or is not fixed at all and subordination issues are not discussed in any way, and everything develops spontaneously.
This principle is difficult to observe if the organization is built on a matrix principle, since in the structure it is impossible to clearly define subordination issues. In this case, the job description determines the area of the employee's functional subordination, and for each project a separate order is issued, where the subordination for this project is indicated.
Powers and responsibility, their conformity.
Powers - this is the degree of authority of the leader, the right to make decisions independently. Responsibility is the achievement of results (indicators) for which the manager is responsible.
A typical situation is when the head does not have the right to solve a certain issue, but if he does not fulfill it, he is responsible (including material ones, for example, this affects his bonuses).
Or vice versa. The manager has the authority, and the responsibility for the results is borne by the superior
As you can see, the reserves of management in the field of optimization of the organizational structure are still sufficient in many organizations. Therefore, the task of the head is to regularly audit the existing structure, to check whether it is adequate to the current goals, whether it prevents any changes. This audit can be carried out in several stages: Identifying the real structure, checking how much the actual structure corresponds to the formally fixed structure. Or, if the structure has not yet been formally fixed, the fixation of the existing structure.
Check the existing structure for compliance with the strategy, as well as the type of organization.
Identification of redundant and missing links, taking into account the stage of development of the organization, its current tasks and basic business processes.
Checking the norm of controllability.
Analysis of co-ordination, identification of zones of dispersion of responsibility.
After such an analysis, a decision is made about the appropriateness of making changes in the organizational structure.
In addition, it is important to take into account the personal aspect of the problem. Quite often, logical and orderly structures remain on paper, do not work. The reason, naturally, is in people. After all, the structure is the totality of the constituent elements of the system and the stable links between them. Accordingly, if we are talking about the structure of an organization, then this is the totality of the elements making up the organization and the stable links between them. The main elements of the organization are people. Therefore, before approving a new structure it is worthwhile to assess how it will be perceived by the key people of the organization, take into account their motives and abilities, enlist support.
CONCLUSION
Hotels and restaurants are not only the most important type of enterprises of economic activity, but also a complex organizational structure characterized by the distribution of goals and tasks of management between whole departments and individual employees.
Advantages of the functional structure:
1) high competence of specialists responsible for the implementation of specific functions;
2) release of line managers from solving some special issues;
3) standardization, formalization and programming of phenomena and processes;
4) elimination of duplication and overlap in the performance of management functions;
5) reduction of the need for specialists of a wide profile.
Disadvantages of the functional structure:
1) excessive interest in the implementation of the goals and objectives of "their" units;
2) difficulties in maintaining the permanent relationships between the various functional services;
3) the emergence of tendencies of excessive centralization;
4) the duration of the decision-making procedures;
5) relatively rigid organizational form, with difficulty responding to changes.
This organizational structure shows that at the highest level they are about 10%, on average - 50% and at the lowest level - about 70% of the total time of managers.
As can be seen from the data in the table, all the indicators considered in the analyzed period demonstrate stable dynamics to growth.
It should be noted that the share of the cost price in the proceeds from the sale of goods, products, works, services in the periods under review is quite stable. The increase in the share of the cost price in the proceeds from the sale of goods, products, works and services was the result of an increase in the cost of purchased raw materials and materials, an increase in tariffs for energy resources.
Factors that affected the change in the amount of proceeds from the issuer's primary business:
To implement the closed technological cycle of customer service, the following main services are provided in the hotel:
• Reservation;
• maintenance;
• reception and calculation part;
• room operation service.
The goal is to increase the manageability and transparency of the business by consolidating the areas of responsibility and authority
Methods of work to optimize the organizational structure of the company:
1. Expert consultation (interview, analysis of documents, data collection)
2. Working sessions
References
1. Andreeva AS, Bondarev A.V. Marketing. - SPb .: Phoenix, 2007. - 580 p.
2. Andreeva O.G. Technology of effective marketing. - Moscow: Unity, 2005. - 456 p.
3. Arkhipova Yu.P. Fundamentals of marketing. - Moscow: Unity, 2006. - 610 p.
4. Arshinova V.G. Marketing strategy. - Moscow: Unity, 2005. - 480 p.
5. Baranov S.A. Marketing for entrepreneurs. - Moscow: Delta, 2003. - 245 p.
6. Bazarov N.P. and Mei V.P. Marketing activity of the enterprise. - Moscow: The Case, 2004.- 450 pp.
7. Babansky Yu.K. Organization of the marketing system. - St. Petersburg: Phoenix, 2007. - 640 p.
8. Bakhrushin Yu.A. Effective management. Economic problems and optimal solutions. - Moscow: Academy, 2005.- 610 p.
9. Benina S.I. Theory, practice and art of management. - Moscow: Academy, 2006.- 430 p.
10. Berkutova M.B. Organization of marketing department at the enterprise. - Minsk. Tiko, 2007. - 580 p.
11. Bogomolova, L. V. The structure of the marketing service. - St. Petersburg: Phoenix, 2005.- 605 p.
12. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation 10/10/2015 N 1085 "On approval of the Rules for Granting hotel services in the Russian Federation "
13. "GOST 30389-2013, Interstate Standard, Services Of public catering and. Classification and general requirements "
(together with the "Minimum requirements for enterprises (objects) of public catering of various types ")
14. GOST R 50764-95 "Public catering services. General requirements"
15. The order of Rosstandart from 11/22/2013 1676-st)








