Lesson 5. 1. Plant, its parts and their function
1. Translate the following sentences containing c ompound Forms of Participle I and Gerund:
a)
1. Being adapted to the conditions of our region, sorghum produces high yields.
2. Having been grown for two years, legumes increased soil fertility.
3. Having completed its life cycle, the plant died;
b)
1. High yield of potatoes was obtained by their having been grown on a good soil.
2. We know of corn being produced both for grain and for silage.
3. The farmer could improve his soil by having provided it with the necessary mineral elements.
2. Find the meaning of the following word combinations in an electronic dictionary.
for instance, because of, in addition, in addition to, to take place, to some extent.
3. Find compound –ing forms in text A and identify their function
Vocabulary Focus

| Handwrite the words and word combinations related to text A and give their Russian equivalents. Check them in the agronomy and soil science. to germinate, seedling, to flower, to mature, leaf (leaves), to reproduce, to lodge, tops, nutrients, resistant, resistance, to control, water, rain, amount, size, storage, to store, underground, to reach, kind, number, to find (found), due, due to, to be due to, the former, the latter, to consist of.dictionaries. |
4. Read aloud and translate text А.
Text 5А
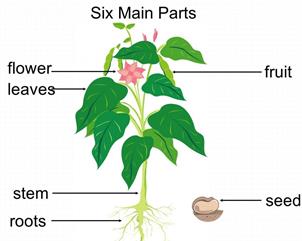
Plant, its parts and their functions
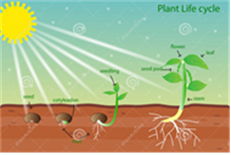
Most of the important crop plants are reproduced by seeds, and they are known as seed plants. In the life cycle of these plants the seed germinates and produces a seedling. The vegetative phase is characterized by increases in the number and size of roots, stems and leaves. Finally, having reached the reproductive phase, the plant flowers and produces seeds, thus completing its life cycle.
Sometimes as much1 as one half, but in certain root crops more than one half of a crop plant is underground. Being in the soil the roots are as important as the tops because nearly all the water and all the mineral nutrients required are absorbed by roots. Having been absorbed from the soil, the nutrients and water are translocated from roots to other plant parts.
In addition to2 the main function mentioned the root performs two more functions. It anchors the plant by branching throughout the soil and serves as a storage organ for nutrients in biennial and perennial plants. Due to their having stored up food during the previous year these plants are able to produce new spring growth.
Two general kinds of roots are found in crop plants: fibrous roots and tap roots. The roots of cereals and other grasses belong to the former and those of legumes and root crops – to the latter. Water and nutrients dissolved in it are absorbed through the root hairs found on roots and root branches of both fibrous rooted and tap rooted plants.
The above ground portion of a plant consists of leaves and stems. The leaf plays a highly important role due to its manufacturing carbohydrates through the process known as photosynthesis.

The main functions of the stem are: conducting water and plant nutrients from root to leaf, supporting leaves and storing food materials as in the case of sugarcane and sorghum.
Being young the grasses have solid stems, that is, the ones filled with the pith. Having matured the stems of most grasses become hollow. Some crops as corn, for instance, have stem pith throughout their lives.
A major crop production problem associated with the stem is lodging which is due to the adverse effects of rain and wind. Resistance to lodging, or the capacity of stems to withstand the adverse effect of weather, is an important quality in cereals. Growing lodging resistant varieties is the main controlling measure.
Notes to the text
1. as much as (перед цифрой) – до, целых;
2. in addition to – кроме;
3. two more – еще две.

| due – надлежащий, соответствующий; due to – из-за; вследствие; благодаря; to be due to – объясняться, обусловливаться. |
 | |||
 | |||
Grammar and vocabulary activities
4. Provide Russian equivalents:
reproduction, normally, physiology, to combine, energy, reaction, genetics, progress, critical, organic, inorganic, to limit, material, method, individual, carbohydrates, botanist, protein.








