Text А Classification of field crops
Crops are variously grouped and classified. For example, they may be classified as cultivated or row crops, such as corn, soybeans and cotton; non-cultivated crops, such as wheat and barley; and hay or pasture crops, such as clovers, alfalfa, and many other small-seeded legumes and grasses.
Crops are also grouped according to2 the duration of their growth. Annual crops are those that complete their life cycle in one season. Biennials start their growth in one season but produce seed and die at the end of the second season. Perennials grow for more than two seasons, producing seed each year.
The most important and most often used classifications are botanical classification and agronomic classification.
Botanical classification.

Botanical classification is based upon similarity of plant parts. Most of our field crops belong to one of the two botanical families, the grasses and the legumes.
The main food plants known belong to the grass family, including all cereal crops and about three fourths3 of the cultivated forage crops. Cereals are the world's leading food and feed crops. They are grain-bearing grasses such as wheat, corn, rye, barley, oats etc.4 Forage grasses are the ones that are highly essential for the economic production of livestock products.
Almost all grasses have hollow stems made up of nodes and internodes and varying greatly in length in different plants. The roots are fibrous. Grasses may be either annuals or perennials.
The legume family includes such large-seeded legumes as field beans, field peas, soybeans and such nutritious forage crops as alfalfa and clovers. The plants of this family are the only6 ones growing in a symbiotic relationship with rhizobia bacteria. Multiplying in the nodules on the roots of the legume crops raised bacteria are able to fix free atmospheric nitrogen in their bodies and eventually in the plant residues. Ploughing under7 these plant residues, one can increase soil fertility. Being high in protein content the legume crops are also valued as food both for man and farm animals.
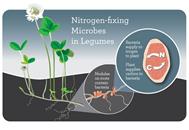
Legumes may be annuals, biennials or perennials. The fruit is a pod containing from one to several seeds. Legumes have tap roots.
There are some other botanical families that include crop plants widely used by man. Such crops are potatoes, sugar beet, cotton, flах, buckwheat and others.
Notes to the text
1. for example – например;
2. according to -– согласно, no;
3. three fourths – три четверти;
4. etc. [it'setre] -– и так далее;
5. made up of – состоящий из;
6. to plough under – запахать.
Remember
 | |||
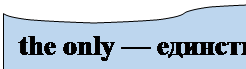 | |||
Grammar and vocabulary activities
7. Translate the following word combinations with nouns as attributes to other nouns:
soil fertility increase, soil air circulation, life cycle duration, mineral fertilizer application, higher protein content, most important plant parts, high-quality hay production, chemical weed control.
8. Identify by suffixes the parts of speech the following words belong to:
agronomically, hybridization, industrial, ventilation, economically, vegetative, characterize, function, intensity, transformation, special, specialist, actively, structure, statistically.
9. Translate the following word combinations containing participles:
leading cereal and forage crops, crops adapted to the conditions of the region, farms growing wheat, some crops grown by our farm, animals supplying people with food, soil supplied with nitrogen, one of the cereal crops raised, crops requiring much nitrogen, number of years required for growth, wheat varieties best known to people, the only crop producing high yields.

10. Highlight the participles in post-position and participle constructions in the following sentences. Translate them:








