Classification of Types of Robot
One way of classifying robots is in terms of their similarity to humans. An automaton is any machine capable of operating independently, such as a clothes dryer. A flexible machine is a special case of an automaton with different capabilities, that can be programmed as the need arises. An example is a welding robot on the factory floor that can be programmed to participate in other production operations. A mobile robot is a flexible machine capable of moving freely in its own environment. It can partly select its own goals and communicates with other agents, including humans. An android or humanoid is a mobile robot whose structure approximately resembles a human structure. Finally, a cyborg is a humanoid with organic structures. Cyborgs have some physiological structures similar to those of humans.
| 1. c Mobile robot 2. c Cyborg 3. c Automaton 4. c Flexible machine 5. c Android/ Humanoid | a) machine capable of independent operation following a predetermined series of behaviours, e.g. a cuckoo clock b) flexible machine capable of moving and communicating with humans, e.g. a sentry robot c) humanoid having both organic and inorganic structures, with some physiological similarity to humans d) mobile robot of human proportions e) versatile, programmable automaton, e.g. an assembly robot |
8.9. Now renumber the robot types, 1–5 (1 = the most similar to humans; 5 = the simplest).
What type of work can each of the types be used for? Provide examples.
8.10. What can these robots do? Say what you think. What type of robot do they belong to?

8.11. Listen to different people talking about the robots to check your answers and number the photos in the order you hear about them.
8.12. Listen again and say which robot:
1. is fully automatic.
2. can reach 15 metres.
3. is an electronic pet.
4. has vacuum gripper feet.
5. is the solution for dirty windows.
6. is designed to save floor space.
The Complex Subject
| Verbs and Word Groups | The Complex Subject | Translation |
| Verb in the Passive: · sense perception: to see, to hear, to notice · mental activity: to think, to consider, to believe, to expect, to suppose, to know · order and permission: to order, to ask, to offer, to tell, to allow, to let, to encourage, to make · reporting: to say, to report, to announce | An old man was seen to walk and play with AIBO like with a real dog. Japanese engineers are believed to develop a new model of AIBO every year. to be developing a new model of AIBO now. to have developed AIBO as an electronic friend for old people. A new model of AIBO is believed to be developed every year. AIBO is believed to have been developed as an electronic friend for old people. The designer was asked to demonstrate the capabilities of the new model of AIBO. Japanese engineers are reported to develop a new model of AIBO every year. | Видели, как пожилой человек гулял и играл … Считается, что японские инженеры конструируют … … сконструировали … Считается, что новую модель конст-руируют … … был сконструирован … Разработчика попросили продемонстрировать … Сообщают, что японские инженеры конструируют … |
Продолжение таблицы
| Verbs and Word Groups | The Complex Subject | Translation |
| Pairs of synonyms: to seem/to appear, to happen/to chance, to prove/to turn out | to be developing a new model of AIBO at the moment. to have developed AIBO as an electronic friend for old people. A new model of AIBO is reported to be developed every year. AIBO is reported to have been developed as an electronic friend for old people. The results of the work don’t seem to satisfy the researchers. The researchers seemed to be satisfied with the results of their work. The two scientists happen to be working on similar projects. A group of first-year students turned out to have developed the robot which won the competition. The robot which won the competition turned out to have been developed by a group of first-year students. | … сконструировали … Сообщают, что новую модель конструируют … … был сконструирован … Кажется, результаты работы не устраивают … Казалось, исследователи были удовлетворены … Эти двое ученых случайно работают … Оказалось, что сту-денты первого кур-са сконструировали … Оказалось, что робот был сконструирован … |
Окончание таблицы
| Verbs and Word Groups | The Complex Subject | Translation |
| Word groups: to be likely, to be unlikely, to be sure/to be certain | Electronic pets are not likely to replace real cats and dogs. Real cats and dogs are unlikely to be replaced by electronic pets. Engineers are likely to be developing robots for using in the home. The designers are sure to have created the robot in order to test their theory. The robot is certain to have been created in order to test some theory. | Электронные домашние любимцы вряд ли заменят … Живых кошек и со-бак вряд ли заменят …. Инженеры, вероятно, конструируют … Конструкторы наверняка создали … Робот, несомненно, был создан … |
8.13. Which is right?
1. Robots are supposed to be used/to be using for doing boring or dangerous jobs.
2. Engineers seem to be working/to have worked on new types of robots that will help doctors perform surgical operations.
3. Robots are known to apply/to have been applied in industry for about 50 years.
4. Scientists are expected to develop/to be developed robotic parts of the body for disabled people.
5. The programmer proved to make/to have made a mistake, that is why the robot soldered the wires in the wrong way.
6. People are not likely to do/to have done any manual work at the highly automated factories of the future.
8.14. Replace the following complex sentences with simple sentences with the Complex Subject.
Model: The developers of the robot dog AIBO say that it understands the name you give it.
AIBO is said to understand the name you give it.
1. People consider that Japanese companies make the most advanced humanoid robots in the world.
2. Aerospace engineers expect that robots will successfully perform different tasks in space.
3. It is likely that the robot being developed by the researches of our laboratory will be used for eye surgery.
4. The journal reports that scientists imitated muscle structure and movement of an elephant's trunk in order to create a robotic arm capable of lifting heavy objects.
5. It appears that the scientists of this research institute are designing nanorobots for drug delivery.
6. It turned out that robots are extremely good at inserting integrated circuits onto printed circuit boards used in electronics.
8.15. Translate the part of the sentence in brackets into English.
1. The idea of creating a mechanical helper seems (появилась) together with the mankind.
2. Robots proved (очень эффективны) in automobile industry.
3. The bomb was reported (была обезврежена) by a robot.
4. Scientists are considered (проектируют) robots that will be able to learn like children.
5. The trains of the future are likely (будут управляться) by robots.
6. By 2050 a team of fully autonomous humanoid robots is expected (смогут обыграть) the human world champion team in soccer.
8.16. Translate into English.
1. Известно, что слово «робот» впервые использовал чешский писатель Карел Чапек, образовав его от чешского слова ‘robota’, означающего тяжелый принудительный труд.
2. Оказалось, что роботы прекрасно выполняют задачи, требующие точных и быстрых повторяющихся движений.
3. Сообщают, что в Массачусетском технологическом институте (Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MIT) разрабатывают роботов, способных учиться, как маленькие дети.
4. Проектируя вакуумные «ноги» этого робота, ученые, скорее всего, пытались имитировать способность ящерицы геккон (gecko) передвигаться по любым поверхностям, даже вертикальным и гладким.
5. Кажется, роботы нашли применение во всех сферах жизни: от упаковки конфет в коробки и сборки автомобильных двигателей до обезвреживания бомб и сложных хирургических операций.
6. В футболе современные роботы вряд ли смогут составить конкуренцию игрокам-людям.
8.17. Using the diagram to help you, fill in the gaps in the text with the words given. Use your dictionary if necessary.
Co-ordination of control in robots
The diagram shows a (1) _____ system for the force required to (2) _____ an object. The desired level of force is fed into the control module, which (3) _____ it with the actual amount of force as indicated by the feedback signal. The discrepancy enters the command generator, which determines the (4) _____ and extent of adjustment necessary. The resulting command passes into an amplifier which produces power (5) _____ to the level of the input signal. The power drives a motor (6) _____ to some linkage such as a set of gears. The mechanical linkage in the robotic hand ultimately (7) _____ the initial command signal into displacement at the fingertips.
proportional grasp attached closed-loop compares direction converts
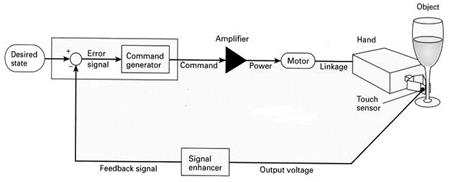
8.18. Using the diagram and the explanation fill in the following table:
| Element of the system | Function |
8.19. Design a robot to do a dangerous or boring job for you. Draw a rough sketch and make notes about how it works.
Model:
| What the robot is for How it works | It is to pick up the socks in my bedroom The sensor smells ..., the arm ... |
8.20. Discuss your ideas with a partner. Comment on your partner's idea.
Model:
What powers the robot? Where does it put the socks?
Unit 9
My Faculty
Vocabulary
1. to enter the University поступить
в университет
2. to take / to pass entrance [´entrәns] сдавать / сдать
exams вступительные экзамены
3. to be admitted to the [әd´mıtıd] быть принятым
faculty на факультет
4. full-time / part-time / дневная / вечерняя /
extramural forms [‚ekstrә´mj|әrәl] заочная формы
of education обучения
5. to be set up быть основанным
(syn. to be founded,
to be formed,
to be organized)
6. to be situated быть расположенным
(syn. to be located)
7. teaching block учебный корпус
8. dean декан
9. dean’s office деканат
10. to take office вступить в должность
11. academic staff [stä:f] профессорско-
(syn. teaching staff) преподавательский состав
12. curriculum (pl. curricula) [kә´rıkj|lәm] учебный план
13. bias (syn. major, [baıәs] [´meıdžә] профилирующие
core) subjects [ké:] предметы
14. general (syn. minor) [´maınә] непрофилирующие
subjects предметы
15. elective courses [ı´lektıv] курсы по выбору
16. instructional [ın´stršk∫n(ә)l учебная
laboratory lә´bãrәt(ә)rı] лаборатория
17. to equip [ı´kwıp] оборудовать
18. to participate [pä:´tısı‚peıt] принимать участие
(syn. to take part)
19. research [rı´ sît∫, ´ri:sî:t∫ ] исследование
20. career-oriented / [kә´rıә ´é:riәntıd] студент,
research-oriented ориентированный
student на практическую /
исследовательскую
деятельность
21. to offer a multi-level предлагать
education scheme [ski:m] многоуровневую
систему образования
22. to award a degree [ә´wé:d] присвоить степень
23. Bachelor’s / Master of [´bæt∫әlә] степень бакалавра /
Science degree / Diploma [dı´plә|mә] магистра /
in Engineering диплом инженера
24. to take a postgraduate [pә|st´grædž|әt] учиться в аспирантуре
course
25. to have practical training проходить практику
26. to graduate from the [´grædžu‚eıt] окончить университет
University
27. graduate [´grædžuәt] выпускник
9.1. Fill in the gaps with information about your faculty. For reference visit http://www.nstu.ru.
The students of our group _____ the University last year. There are _____ faculties at NSTU. I was admitted to _____. Our faculty was set up in _____. The dean’s office is situated in teaching block _____. The dean of our faculty is _____. He took office in _____. The _____ includes _____ professors and teachers.
Minor subjects are studied in the first and second year. Students begin to study _____ in the third year. They can also choose _____ courses.
The faculty offers a _____ education scheme. It takes students four years to get a _____ degree. Research-oriented students can continue their studies, _____ in scientific research and be awarded a _____ degree. Graduates can take a _____ course.
Students have practical training in _____. After graduating from the University I am going to work in _____.
9.2. What are synonyms of the following words?
1. to be founded
2. to be situated
3. academic staff
4. general subjects
5. bias subjects
6. to participate
9.3. Match the items and their opposites
| 1. to graduate from the University 2. to fail the exams 3. minor 4. career-oriented 5. one-level education scheme | a) research-oriented b) to enter the university c) multi-level education scheme d) major e) to pass exams |
9.4. Make up all possible word combinations. Make sentences with the combinations.
| 1. academic 2. to award 3. dean’s 4. to enter 5. to have 6. instructional 7. major 8. to pass 9. to take 10. teaching | a) block b) a course c) a degree d) an exam e) laboratory f) office g) practical training h) staff i) subject j) a university |
9.5. Read and translate the names of the faculties. Which of them do you study at?
| Aircraft [´eә‚krä:ft] Applied Mathematics and Information Science [ә‚plaıd mæθә´mætıks әnd ‚ınfә‚meı∫n ´saıәns] Automation and Computer Engineering [‚é:tә´meı∫n әnd kәm‚pju:tә ‚endžı´nıәrıŋ] Business Administration [´bıznәs әd‚mını´streı∫n] Humanities [hju:´mænәtiz] | Mechanics and Technology [mı´kænıks әnd tek´nãlәdži] Mechatronics and Automation [‚mekә´trãnıks әnd ‚é:tә´meı∫n] Physical Engineering [‚fızıkl ‚endžı´nıәrıŋ] Power Engineering [‚pa|ә ‚endžı´nıәrıŋ] Radio Engineering, Electronics and Physics [‚reıdiә| ‚endžı´nıәrıŋ ‚elek´trãnıks әnd ´fızıks] |
9.6. Answer the following questions.
1. How many faculties are there at NSTU?
2. Which faculty were you admitted to?
3. What forms of education does your faculty offer?
4. When was your faculty set up?
5. Where is your dean’s office situated?
6. Who is your dean?
7. When did he take office?
8. What general subjects of the curriculum are studied by the first-year students?
9. When do students begin to study major subjects?
10. Are there elective courses at your faculty?
11. What are instructional laboratories equipped with?
12. What education scheme does your faculty offer?
13. Are you a research- or a career-oriented student?
14. How long does it take students to get a Bachelor’s degree?
15. When is a Master’s degree awarded?
16. Do students of your faculty participate in scientific research?
17. Where can you take a postgraduate course?
18. Where do students of your faculty have practical training?
19. Where do the graduates of your faculty work?
20. Where are you going to work after graduating from the University?
9.7. Translate into English. Fill in the gaps in Sentence 7 with information about your faculty and speciality.
1. Факультет готовит специалистов в широком спектре областей, так что каждый студент может легко выбрать область специализации.
2. Студенты учатся профессионально использовать и обслуживать современное оборудование, чтобы эффективно применять его в своей учебной, исследовательской и практической деятельности.
3. Студентам предоставляется возможность не только получить самые современные знания в выбранной области, но и выполнять исследования и участвовать в инженерных разработках.
4. В соответствии с многоуровневой системой образования, введенной на факультете, студентам, успешно окончившим курс обучения, присуждается степень бакалавра, магистра или диплом инженера.
5. Квалификация, полученная на факультете, позволит выпускникам найти хорошую работу в выбранной сфере.
6. Выпускники, имеющие степень магистра или диплом инженера и ориентированные на научную деятельность, могут поступить в аспирантуру и получить ученую степень кандидата наук.
7. Студенты, специализирующиеся в _____, обучаются _____, и после окончания университета смогут работать в сфере _____.
9.8. Match the words and their definitions.
| 1. day release 2. to drop out 3. tough 4. mock 5. binary 6. to be keen on sth 7. to assess 8. strict | a) to make a judgment after considering carefully b) using combinations of the numbers 0 and 1 c) a system by which workers spend one day a week at a college to study a subject related to their work d) to leave before finishing what was intended to do e) to be interested in sth and enjoy it f) not real but intended to look or seem real g) expecting people to obey rules completely h) difficult |
9.9. You are going to hear an interview with Alan, a Scottish student of electronics at a college of higher education. Here are some of Alan’s answers. What were the questions?
1. _____?
Nineteen.
2. _____?
It's a National Certificate in Information Technology.
3. _____?
Full-time.
4. _____?
A year. It finishes at the end of June.
5. _____?
Twelve.
6. _____?
Electrical Principles, Digital and Analogue Electronics. These are first thing in the morning. Then we've got Communications.








