Engineering Materials
Engineers have to know the best and most economical materials to use. Engineers must also understand the properties of these materials and how they can be worked. There are two kinds of materials used in engineering – metals and non-metals. We can divide metals into ferrous and non-ferrous. The former contain iron and the latter do not contain iron. Cast iron and steel, which are both alloys, or mixtures of iron and carbon, are the two most important ferrous metals. Steel contains a smaller proportion of carbon than cast iron. Certain elements can improve the properties of steel and are therefore added to it. For example, chromium may be included to resist corrosion and tungsten to increase hardness. Aluminium, copper, and the alloys (bronze and brass) are common non-ferrous metals.
Plastics and ceramics are non-metals; however, plastics may be machined like metals. Plastics are classified into two types – thermoplastics and thermosets. Thermoplastics can be shaped and reshaped by heat and pressure but thermosets cannot be reshaped because they undergo chemical changes as they harden. Ceramics are often employed by engineers when materials which can withstand high temperatures are needed.
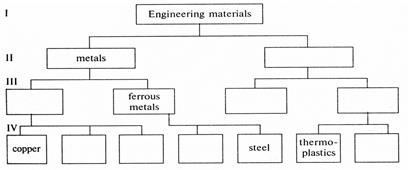
6.7. Draw similar diagrams displaying the connection between the following:
1. alloys, copper, brass, pure metals, aluminium, metals;
2. computer system, CPU, hardware, main memory, peripherals, software;
3. aeronautical engineering, civil engineering, electrical engineering, engineering, heating and ventilating, marine engineering, mechanical engineering.
6.8. Use the diagrams and the following table to classify the things described.
Classification
| There are | two three several many | types kinds sorts classes varieties | of materials | ||
| Materials | are of fall into | ||||
| We can | classify divide split | materials | into several | classes categories groups types | according to… |
| Engineering materials | consist of include | metals and non-metals | |||
6.9. Match the symbols of chemical elements, their English names and their Russian equivalents. What are the properties of engineering materials containing these elements?
Fe tungsten [´tšŋstәn] алюминий
C titanium [taı´teıniәm] молибден
Cr tin [tın] вольфрам
W nickel [nıkl] марганец
Al molybdenum [mә´lıbdәnәm] кобальт
Cu manganese [´mæŋgә‚ni:z] углерод
Mn iron [´aıәn] железо
Ni copper [´kãpә] никель
Sn cobalt [´kә|‚bé:lt] олово
Co chromium [´krә|miәm] титан
Mo carbon [´kä:bәn] хром
Ti aluminium [‚ælә´mıniәm] медь
6.10. Join the pairs of sentences using however, therefore, because. Follow the models:
Model 1
Copper does not rust.
Copper corrodes.
(a + b) Copper does not rust; however it corrodes.
Model 2
Cast iron is a brittle metal.
Cast iron is not used to withstand impact loads.
(a + b) Cast iron is a brittle metal, therefore it is not used to withstand impact loads.
Model 3
Titanium is used for aircraft frames.
Titanium is light and strong.
(a + b) Titanium is used for aircraft frames because it is light and strong.
1. Chromium resists corrosion. Chromium is added to steels to make them rust-proof.
2. Manganese steel is very hard. Manganese steel is used for armour plate.
3. Bronze has a low coefficient of friction. Bronze is used to make bearings.
4. Nylon is used to make fibres and gears. Nylon is tough and has a low coefficient of friction.
5. Tin is used to coat other metals to protect them. Tin resists corrosion.
6. Tin is expensive. The coats of tin applied to other metals are very thin.
7. Stainless steels require little maintenance and have a high strength. Stainless steels are expensive and difficult to machine at high speeds.
8. Nickel, cobalt and chromium improve the properties of metals. Nickel, cobalt and chromium are added to steels.
6.11. Join the following sentences into one using the connectors in brackets. You may omit or replace any parts if that is necessary to retain the structure of an English sentence.
Model:
because/and/however
Plastics are used widely in engineering. They are cheap. They have resistance to atmospheric corrosion. Plastics are not particularly strong.
Plastics are used widely in engineering because they are cheap and have resistance to atmospheric corrosion; however, they are not particularly strong.
1. and: There are two types of plastics. Thermoplastics are plastics. Thermosets are plastics.
2. and/whereas /and: Thermoplastics will soften when heated. Thermoplastics will harden when cooled. Thermosets set on heating. Thermosets will not remelt.
3. from/to: Plastics are used to make a great variety of products. Plastics are used to make textiles. Plastics are used to make engineering components.
4. such as: Plastics are available in many forms. Plastics are available in the form of sheets, tubes, rods, moulding powders and resins.
5. to: Various methods are used. These methods convert raw plastic into finished products. Compression moulding is a common method. Compression moulding is used for shaping thermosets.
6. with/which: The equipment consists of a press. The press has two heated platens. The two heated platens carry an upper and a lower mould.
7. then: Powder is placed in the lower mould. This is moulding powder. The upper mould is pressed down on the lower mould.
8. to/which: The pressure and the heat change the powder. The powder becomes liquid plastic. The liquid plastic fills the space between the moulds.
9. when/and: The chemical changes have taken place. The mould is opened. The moulding is extracted.
10. by: Plastic bowls are made. The compression moulding method is used.
6.12. Translate into English.
1. Как металлы, так и неметаллы обладают определенными свойствами, обусловливающими их пригодность для использования в конкретных целях.
2. Хром может быть добавлен в сталь для повышения качества режущей кромки.
3. На определенной стадии производства пластмассы жидкие, но в готовых изделиях они твердые.
4. Материалы с низким коэффициентом трения используются для изготовления подшипников.
5. Устойчивые к коррозии материалы используются в качестве защитного покрытия для металлов.
6. Метод компрессионного формования используется для изготовления различных изделий из порошков.
6.13. What are the properties and uses of metals? Fill in the appropriate part of the table.
| Materials | Properties | Uses |
| Metals | ||
| Non-metals |
Now listen to the text and add new information to your notes.
6.14. Make a list of properties of non-metals keeping in mind that they are opposite to the properties of metals.








