3. Protein Synthesis occurs in two parts. Part I – Transcription
1. mRNA (………) travels from the cell`s cytoplasm into the nucleus
2. In the nucleus DNA………..
3. mRNA ……………float into unzipped DNA following the order of the nitrogenous bases.
4. mRNA carries DNA`s code, in it`s strand out into …………..
5. In the cytoplasm mRNA joins with tRNA for ext step…………
Part II – Translation
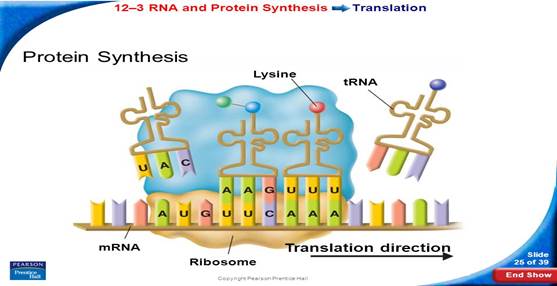
1. mRNA travels to and joins to a ribosomal unit at the 5` untranslated region.
2. A …………(looks like a clover leaf) carrying a “start”………and the amino acid attaches to the codon on the mRNA.
3. The ……… moves in the 3` direction down the messenger RNA by three bases or one codon shifting the t RNA and protein .
4. tRNA ejected from the ribosome.
5. Process continues until a “stop” codon is reached which finishes the process releasing the ………
4. Decide crossword 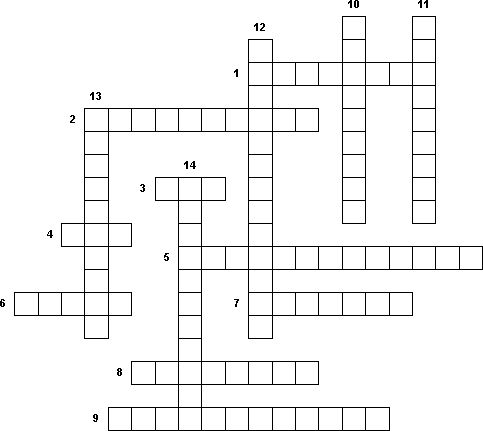
1. Specific sequence of nucleotides at the beginning of each gene.
2. Transition of the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA molecule to the sequence of the AK molecule of the protein.
3. Sign of the beginning of the broadcast.
4. The carrier of genetic information, located in the cell nucleus.
5. The property of the genetic code, which increases the reliability of storage and transmission of genetic information in cell division.
6. A section of DNA containing information on the primary structure of a single protein.
7. A sequence of three consecutive nucleotides of DNA.
8. All ribosomes that synthesize a protein on one molecule of mRNA.
9. The process of translating information about the sequence of AK in the protein from the "DNA language" to the "RNA language".
10. A codon that does not encode AK, but only shows that protein synthesis must be completed.
11. Structure, where the sequence of AK in the protein molecule is determined.
12. An important property of the genetic code, that is, one triplet always encodes only one AK.
13. "Punctuation mark" in the DNA molecule, indicating that the synthesis of mRNA should be stopped.
14. Genetic code ... for all living organisms from bacteria to humans.
5. Compare this sentences:
A. Protein synthesis 1. occurs in the cell nucleus
B. RNA 2. consists of proteins and ribosom RNA molecules
C. The ribosome 3. molecule possess a specific sequence of 3-bases (anti-codon)
D. tRNA 4. process whereby biological cells generate new proteins
E. Transcription 5. copy of the protein genetic information encoded in DNA
Answers:
Horizontally
2. hormones
5. polysome
9. coenzymes
14. anticodon
16. chromatin
17. amino acid
20. ribosome
21. translation
Vertically
1. enzymes
2. glucose
3.vitamins
4. ribosomes
6. matrix
7. biosynthesis
8. glycolysis
10. terminator
11. cytoplasm
12 kodon
13. monomer
15. nucleotide
18. mitochondria
19, transcription
22. replication
23. nucleolus
2. mRNA
tRNA
Guanine Adenine Cytosine Uracil
3. part I 1.messenger 2. Unzips 3. Cytoplasm 4. Translation
Part II 1. tRNA 2. Codon 3. Ribosome 4. Protein
4.
1. Promoter
2. translation
3. AUG
4. DNA
5. degeneracy
6. genome
7. triplet
8. polysome
9. transcription
10. stop kodon
11. primary
12. specificity
13. terminator
14. universal
5. A – 4 B – 5 C – 2 D – 3 E - 1








