What is intellectual disability?
Project task
1. Print the text at Microsoft Word about defectology using text formatting.
2. Make your biography with your photo
3. Create your visit-card
4. Make an invitation using Word Art object
5. Make a resume
The American Association on Mental Retardation gives the following definition: [2]
Mental retardation (MR) refers to substantial limitations in present functioning. It starts before age 18 and is characterized by significantly subaverage intellectual functioning, existing concurrently with related limitations in two or more of the following applicable adaptive skill areas:
· communication
· self-care
· home living
· social skills
· community use
· self-direction
· health and safety
· functional academics
· leisure
· work
 Traditionally, MR has been classified into 5 categories:
Traditionally, MR has been classified into 5 categories:
· mild MR – IQ from (50-55) to 70
· moderate MR – IQ from (35-40) to (50-55)
· severe MR – IQ from (20-25) to (35-40)
· profound MR – IQ below (20-25)
· MR, severity unspecified – this is diagnosed when there is a strong suspicion of Intellectual disability (ID), once called mental retardation, is characterized by below-average intelligence or mental ability and a lack of skills necessary for day-to-day living. People with intellectual disabilities can and do learn new skills, but they learn them more slowly. There are varying degrees of intellectual disability, from mild to profound.
What is intellectual disability?
Someone with intellectual disability has limitations in two areas. These areas are:
- Intellectual functioning. Also known as IQ, this refers to a person’s ability to learn, reason, make decisions, and solve problems.
- Adaptive behaviors. These are skills necessary for day-to-day life, such as being able to communicate effectively, interact with others, and take care of oneself.
IQ (intelligence quotient) is measured by an IQ test. The average IQ is 100, with the majority of people scoring between 85 and 115. A person is considered intellectually disabled if he or she has an IQ of less than 70 to 75.
What are the signs of intellectual disability in children?
There are many different signs of intellectual disability in children. Signs may appear during infancy, or they may not be noticeable until a child reaches school age. It often depends on the severity of the disability. Some of the most common signs of intellectual disability are:
- Rolling over, sitting up, crawling, or walking late
- Talking late or having trouble with talking
- Slow to master things like potty training, dressing, and feeding himself or herself
- Difficulty remembering things
- Inability to connect actions with consequences
- Behavior problems such as explosive tantrums
- Difficulty with problem-solving or logical thinking
In children with severe or profound intellectual disability, there may be other health problems as well. These problems may include seizures, mood disorders (anxiety, autism, etc.), motor skills impairment, vision problems, or hearing problems.
What causes intellectual disability?
Anytime something interferes with normal brain development, intellectual disability can result. However, a specific cause for intellectual disability can only be pinpointed about a third of the time.
The most common causes of intellectual disability are:
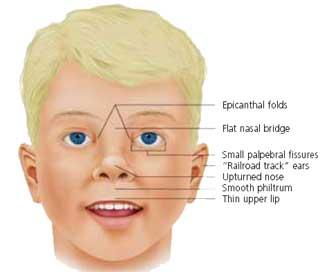
- Genetic conditions. These include things like Down syndrome and fragile X syndrome.
- Problems during pregnancy . Things that can interfere with fetal brain development include alcohol or drug use, malnutrition, certain infections, or preeclampsia.
- Problems during childbirth . Intellectual disability may result if a baby is deprived of oxygen during childbirth or born extremely premature.
- Illness or injury. Infections like meningitis, whooping cough, or the measles can lead to intellectual disability. Severe head injury, near-drowning, extreme malnutrition, infections in the brain, exposure to toxic substances such as lead, and severe neglect or abuse can also cause it.
- None of the above. In two-thirds of all children who have intellectual disability, the cause is unknown.