Изучение алгоритма электронной цифровой подписи (ЭЦП)
Цель работы: изучить алгоритм электронной цифровой подписи
Задание: написать программу, реализующую алгоритм DSA.
Ход работы
DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm) — алгоритм с использованием открытого ключа для создания электронной подписи, но не для шифрования. Поскольку подписываемые документы — переменного (и как правило достаточно большого) объёма, в схемах ЭП зачастую подпись ставится не на сам документ, а на его хеш. Для вычисления хэша используются криптографические хеш-функции, что гарантирует выявление изменений документа при проверке подписи. Вместе с DSA часто используется хеш-функция SHA-1.
Пусть H(x) – хеш-функция, q – большое простое число, размерность которого N в битах совпадает с размерностью в битах значений хэш-функции H, р – простое число такое, что (р-1) делится на q (битовая длина p обозначается L), g – число, мультипликативный порядок которого по модулю p равен q. Для его вычисления можно воспользоваться формулой 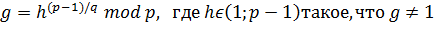 . Тогда:
. Тогда:

Листинг:
#include <CkCrypt2.h>
#include <CkDsa.h>
void ChilkatSample(void)
{
bool success;
// Use Chilkat Crypt to hash the contents of a file.
CkCrypt2 crypt;
success = crypt.UnlockComponent("Anything for 30-day trial.");
if (success != true) {
printf("%s\n",crypt.lastErrorText());
return;
}
crypt.put_EncodingMode("hex");
crypt.put_HashAlgorithm("sha-1");
const char * hashStr;
// Return the SHA-1 hash of a file. The file may be any size.
// The Chilkat Crypt component will stream the file when
// computing the hash, keeping the memory usage constant
// and reasonable.
// The 20-byte SHA-1 hash is returned as a hex-encoded string.
hashStr = crypt.hashFileENC("hamlet.xml");
CkDsa dsa;
// The Chilkat Crypt and Chilkat DSA components are separate
// products. To license both, it's least expensive to purchase
// the "Chilkat Bundle" which provides licenses to all the
// Chilkat components.
success = dsa.UnlockComponent("Anything for 30-day trial");
if (success != true) {
printf("%s\n",dsa.lastErrorText());
return;
}
// Load a DSA private key from a PEM file. Chilkat DSA
// provides the ability to load and save DSA public and private
// keys from encrypted or non-encrypted PEM or DER.
// The LoadText method is for convenience only. You may
// use any means to load the contents of a PEM file into
// a string.
const char * pemPrivateKey;
pemPrivateKey = dsa.loadText("dsa_priv.pem");
success = dsa.FromPem(pemPrivateKey);
if (success != true) {
printf("%s\n",dsa.lastErrorText());
return;
}
// You may optionally verify the key to ensure that it is a valid
// DSA key.
success = dsa.VerifyKey();
if (success != true) {
printf("%s\n",dsa.lastErrorText());
return;
}
// Load the hash to be signed into the DSA object:
success = dsa.SetEncodedHash("hex",hashStr);
if (success != true) {
printf("%s\n",dsa.lastErrorText());
return;
}
// Now that the DSA object contains both the private key and hash,
// it is ready to create the signature:
success = dsa.SignHash();
if (success != true) {
printf("%s\n",dsa.lastErrorText());
return;
}
// If SignHash is successful, the DSA object contains the
// signature. It may be accessed as a hex or base64 encoded
// string. (It is also possible to access directly in byte array form via
// the "Signature" property.)
const char * hexSig;
hexSig = dsa.getEncodedSignature("hex");
printf("Signature:\n");
printf("%s\n",hexSig);
// -----------------------------------------------------------
// Step 2: Verify the DSA Signature
// -----------------------------------------------------------
CkDsa dsa2;
// Load the DSA public key to be used for verification:
const char * pemPublicKey;
pemPublicKey = dsa2.loadText("dsa_pub.pem");
success = dsa2.FromPublicPem(pemPublicKey);
if (success != true) {
printf("%s\n",dsa2.lastErrorText());
return;
}
// Load the hash to be verified against the signature.
success = dsa2.SetEncodedHash("hex",hashStr);
if (success != true) {
printf("%s\n",dsa2.lastErrorText());
return;
}
// Load the signature:
success = dsa2.SetEncodedSignature("hex",hexSig);
if (success != true) {
printf("%s\n",dsa2.lastErrorText());
return;
}
// Verify:
success = dsa2.Verify();
if (success != true) {
printf("%s\n",dsa2.lastErrorText());
}
else {
printf("DSA Signature Verified!\n");
}
}
Вывод: я изучил алгоритм DSA.
лабораторная работа №4








