The energy radiated from a unit surface area of the body per unit time in thefrequency range of unit width is called:spectral density of energy luminosity
The electromagnetic light wave is called unpolarized when:directions of oscillations of vectors 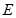 and
and 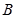 in this wave can lie in any planesperpendicular to the velocity vector of the wave propagation
in this wave can lie in any planesperpendicular to the velocity vector of the wave propagation
The essence of the internal photoelectric effect:under the influence of light incident on semiconductors and dielectrics, electronsare released from their atoms and become free
The expression 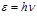 is called:the Planck formula
is called:the Planck formula
The expression 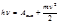 is called:Einstein's formulas
is called:Einstein's formulas
The expression 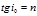 is called:Brewster's law
is called:Brewster's law
The expression 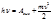 is called:Einstein's formulas
is called:Einstein's formulas
The expression 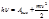 is called:Einstein's formulas
is called:Einstein's formulas
This formula use 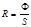 for determining:luminosity
for determining:luminosity
The focal length is:d istance from the center of the lens to the main focus
The formula for the quantum of energy: 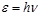
The formula of the strength of light: 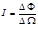
The formula 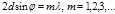 :Wulf-Bragg
:Wulf-Bragg
The polarization of light is:a set of phenomena of wave optics, in which the transverse nature ofelectromagnetic light waves
The formula by which the pressure of light on a white surface is determined: 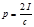
The formula 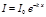 expresses the law:Bouguer-Lambert
expresses the law:Bouguer-Lambert
The formula 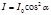 expresses the law:Malusa
expresses the law:Malusa
The formula 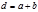 is defined:grating constant
is defined:grating constant
The formula 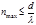 is defined:the maximum order of the spectrum given by the diffraction grating
is defined:the maximum order of the spectrum given by the diffraction grating
The formula 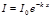 is the law:Bouguer-Lambert
is the law:Bouguer-Lambert
The formula of a thin lens is: 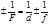
The full reflection condition is equal to: 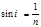
The glass plate, on whose surface are plotted on the principle of the location ofthe Fresnel zones, alternating transparent and opaque rings with radii determinedfor given values, is called:zone plate
The Huygens-Fresnel principle is as follows:the wave surface at any time is not just an envelope of secondary waves, but theresult of their interference
The index of refraction of the medium relative to the vacuum:absolute refractive index
The intensity of light transmitted through two polarizers is determined by the Formula: 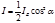
The intensity of the scattered light is inversely proportional to the fourth power ofthe wavelength of the exciting light. This is the wording of the law:Rayleigh
The Lambert law has the form: 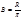
The law of illumination for a surface illuminated by parallel rays: 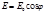
The light from an electric bulb with a light intensity 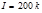 д falls at anangle
д falls at anangle 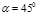 to the workplace, creating an illumination of Е =141lx At what distancer from the workplace is the light bulb? At what height h from the workplace is ithanging?
to the workplace, creating an illumination of Е =141lx At what distancer from the workplace is the light bulb? At what height h from the workplace is ithanging? 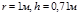
The light flux is:the power of the visible part of the radiation propagating within a given solidangle, estimated from the effect of this radiation on the eye
The light with all possible equiprobable directions of oscillations of a vector 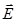 and
and 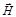 are:unpolarized
are:unpolarized
The light, directions of oscillations of vectors 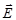 ,
, 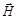 , which is predominant underthe influence of external influences is:partially polarized
, which is predominant underthe influence of external influences is:partially polarized
The light with an ordered direction of vibration of vectors 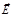 ,
, 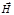 н is:polarized
н is:polarized
The light, directions of oscillations of vectors 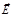 ,
, 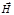 , which describe an ellipselying in a plane perpendicular to the ray is:elliptically polarized
, which describe an ellipselying in a plane perpendicular to the ray is:elliptically polarized
The light in which the vector 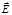 oscillates only in one direction perpendicular tothe ray is called:plane-polarized
oscillates only in one direction perpendicular tothe ray is called:plane-polarized
The luminosity R and brightness B are related by: 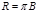 the magnitude of this area
the magnitude of this area
The main focus is called:point on the main optical axis, in which the refracted beams intersect convergingrays incident on the lens parallel to the main optical axis
The main optical axis is:a straight line passing through the centers of the spherical surfaces of the lens
The main maxima of the diffraction of light on the diffraction grating areobserved under the condition: 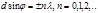
The maximum order of the spectrum given by the diffraction grating isdetermined by the formula: 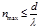
The measure of the solution of some conical surface is called:solid angle
The optical power of the lens is:inverse of the focal length
The optical power depends on:the refractive index of the lens and the radius of curvature of the sphericalsurfaces that bound the lens
The power of the visible part of the radiation propagating within a given solidangle, estimated by the action of this radiation on the eye, is called:light flux
The point at which rays collected after refraction are incident parallel to the mainoptical axis is called:the main focus of the lens
The phenomenon of light used in photography: chemical action of light
The phenomenon of the deviation of light from rectilinear propagation, when light, passing around an obstacle, comes into the region of a geometric shadow, is called:diffraction of light
The photon energy is determined by the formula: 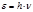
The photon momentum is determined by the formula: 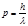
The photon momentum 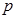 of the red light rays is (
of the red light rays is ( 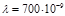 м):
м): 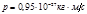
The Planck constant 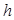 is:
is: 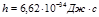
The plane passing through a vector 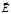 and a ray is:plane of polarization
and a ray is:plane of polarization
The plane passing through the focus perpendicular to the main optical axis is:focal plane
The point at which rays collected after refraction are incident parallel to the mainoptical axis is called:the main focus of the lens
The plane passing through the ray and located perpendicular to the direction ofoscillations 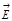 is called:plane of polarization
is called:plane of polarization
The plane passing through the ray and located perpendicular to the direction ofoscillations 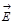 is called:plane of polarization
is called:plane of polarization
The point at which rays collected after refraction are incident parallel to the mainoptical axis is called:the main focus of the lens
The polarization plane of light transmitted by the polarizer is called:the main plane of the polarizer (analyzer)
The power of light is:the ratio of the light flux to the value of the solid angle
The principal minima in the diffraction of light by the diffraction grating areobserved under the condition: 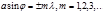
The prismatic spectrum is:strip colored in continuously alternating colors
The process of the transformation of light by matter, accompanied by a change in the direction of light propagation and the appearance of an improper glow of matter, is called:light scattering
Point the unit of measurement of the intensity of light: 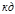
The product of the geometric path length of a light wave in a given medium to therefractive index of this medium is called:optical path length
The difference of the paths traversed by the wave from sources of coherent wavesto the point of space in which interference is observed is called:geometric path difference
The propagation of light rays in the medium occurs independently of each other,individual rays of light, crossing, do not interact. This is the wording:law of independence of light beams
The quantitative characteristic of the light dispersion is:refractive index dispersion
The quantum of energy 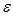 is expressed by the formula:
is expressed by the formula: 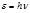
The quantum of energy is expressed: 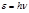
The radiation power of an absolutely black body is N= 34 к Wt. Find the temperature T of this body if it is known that its surface S= 0,6 м 2 . 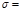 5,67 × 10-8
5,67 × 10-8 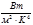 :Т =10000 К
:Т =10000 К
The radii of the curvature of the surfaces of a biconvex lens are given in 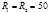 Refractive index of the lens material
Refractive index of the lens material 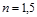 . Find the optical strength
. Find the optical strength 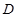 of thelens:D=2 diopter
of thelens:D=2 diopter
The radii of the Newton light rings are determined by the formula:in the transmitted light 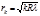
The radius of curvature of the concave mirror is R = 20 cm. At a distance of а1 = 30 cm from the mirror, an object of height y1=1 cm is placed. Find the image distance from mirror а2 and image height y2:а 2 = -15 см ; y2 =5 мм
The radius of the outer boundary of the 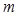 -Fresnel zone is determined by theFormula:
-Fresnel zone is determined by theFormula: 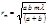
The ratio of the absolute refractive index of the second medium 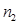 to the absolute refractive index of the first medium
to the absolute refractive index of the first medium 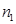 is called:relative index of refraction
is called:relative index of refraction
The ratio of the angle of view obtained by the instrument to the angle of view underwhich the object is visible to the naked eye is called:an increase in the optical device
The Rayleigh law has the form: 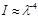
The red border for pure silver is determined by the wavelength 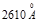 . Find the workfunction of electrons (in eV):4,7 eV
. Find the workfunction of electrons (in eV):4,7 eV
The red border of the photoelectric effect:the minimum frequency 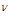 at which the external photoelectric effect begins
at which the external photoelectric effect begins
The refractive index variance is denoted by: 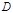
The set of phenomena of wave optics, in which the transverse nature of electromagnetic light waves is manifested, is called:light polarization
The spectral absorptivity is determined by the formula: 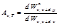
The spectral density of the energy luminosity is determined by the formula: 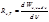
The spectral density of the energy luminosity is called:the energy emitted from a unit surface area of the body per unit time in thefrequency range of unit width
The Stefan-Boltzmann constant 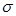 is equal to:
is equal to: 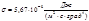
The Stefan-Boltzmann law is expressed by the formula: 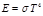
The Stefan-Boltzmann law: 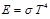
The strength of light from a point source 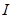 is:a quantity numerically equal to the light flux that this source creates in a unit solidangle
is:a quantity numerically equal to the light flux that this source creates in a unit solidangle
The strength of light is determined by the formula: 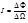
The thickness of the antireflective film is determined by the formula: 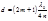
The thin lens formula: 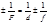
The transparent body, bounded by two spherical or spherical and flat surfaces andtransforming the shape of the light beam, is called:lens
The convex mirror has a radius of curvature of 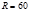 cm. At a distance of
cm. At a distance of 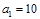 cmfrom the mirror, an object is placed in height
cmfrom the mirror, an object is placed in height 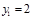 . Find the position
. Find the position 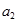 and height
and height 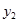 of the image:
of the image: 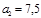 с m,
с m, 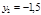 с m
с m
The point at which rays collected after refraction are incident parallel to the main optical axis is called:the main focus of the lens
The unit of measurement of brightness is: 
The unit of measurement of illumination: 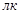
The unit of measurement of the intensity of light is: 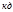
The unit of measurement of the light flux is: 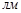
The unit of measurement of the optical force is:diopter
The value 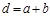 is called:the period (constant) of the diffraction grating
is called:the period (constant) of the diffraction grating
The value of the Planck constant 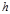 :
: 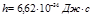
The value of the Stefan-Boltzmann constant  :
: 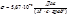
The value of the Stefan-Boltzmann: 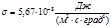
The wavefront is called:the geometric locus of points to which oscillations reach a certain point in time
The wavelength of light corresponding to the red boundary of the photoelectric effect is, for some metal,  l 0 = 275 нм. Find the minimum energy e 0 of the photon causing the photoelectric effect:4.5 eV
l 0 = 275 нм. Find the minimum energy e 0 of the photon causing the photoelectric effect:4.5 eV
The Wolf-Bragg formula: 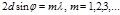
The zone plate is:glass plate, on the surface of which are plotted on the principle of thearrangement of Fresnel zones, alternating transparent and opaque rings with radii determined for given values
This formula 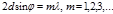 is the formula:Wulf-Bragg
is the formula:Wulf-Bragg
To which section of physics does optics belong?electrodynamics
Two coherent monochromatic light sources are 1 mm apart and emit light with a wavelength of 0.5 mm. At what distance should a screen be placed from them, so that adjacent light interference strips are on it at a distance of 2 mm from each other:4 m
UUU
Under what condition is the image of the object given by the collecting lens
Under what condition is the image of the subject given by the collecting lensobtained imaginary?  less
less 
Unit of lighting:suite
Unit of luminous flux:lumen
Unit of measurement of luminosity: 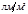
Unit of measurement of the optical power of the lens:diopter
WWW
What angle between the planes of two nicols, the illumination on the screen, createdby the light transmitted through them, decreases by a factor of 4 compared to theillumination caused by light transmitted only through the polarizer: 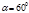
What are coherent waves:waves with the same frequency and unchanged phase difference
What chemical effect of light is manifested in:photosynthesis
Which optical set will be obtained from the microscope, if in it the lens and the eyepiece are interchanged:telescope
What phenomenon is used for photosynthesis:chemical action of light
What determine this 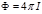 :the total luminous flux that emits a light source
:the total luminous flux that emits a light source
What does the absolute refractive index show: how many times the speed of light in a vacuum 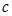 is greater than the speed of light
is greater than the speed of light 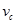 in a given medium
in a given medium
What is the absorption spectrum of a substance:the dependence of the monochromatic natural absorption coefficient on the wavelength
What name the absorption spectrum of isolated atoms:line spectrum
What is Brewster's Law?: 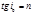
What is the brightness:the ratio of the intensity of light within an elementary solid angle, resting on thearea to the area of the projection of this area on a plane perpendicular to thedirection of the ray
What is the energy luminosity R Э has an absolutely black body, if the maximum
What is the focal length 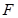 of the lens projecting onto the screen the spectrumobtained by means of a diffraction grating, so that the distance between the twolines of potassium,
of the lens projecting onto the screen the spectrumobtained by means of a diffraction grating, so that the distance between the twolines of potassium, 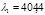 nm and
nm and 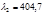 nm, in the first-order spectrum isequal to
nm, in the first-order spectrum isequal to 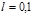 mm? The lattice constant is
mm? The lattice constant is 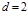 mkm:F=0,65m
mkm:F=0,65m
What is the focal length:distance from the center of the lens to the main focus
What is the red border of the photoelectric effect:the minimum frequency 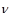 at which the external photoelectric effect begins
at which the external photoelectric effect begins
What is the light flux:the power of the visible part of the radiation propagating within a given solidangle, estimated from the effect of this radiation on the eye
What is the main optical axis:straight line passing through the centers
What is the optical power of the lens:inverse of the focal length
What should be the illumination of the E sheet of paper so that its brightness is equal to В =104 кд/ м 2, if the reflection coefficient is 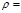 0,75:Е =4,2 × 104 лк
0,75:Е =4,2 × 104 лк
What statement is correct:light manifests itself both as an electromagnetic wave and as a stream of particles
The constant of the diffraction grating is d = 2,5 мкм. Find the angular dispersion of
which diffraction of light occurs (glass plate)
Which scientist first measured speed astronomically?Remer
What phenomenon of light is used in photography:chemical action of light
When the wavelength increases, the refractive index of the medium increases. Whatis this:anomalous dispersion
Who first discovered in 1669 the birefringence:Bartholin








