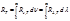MMM-NNN Medium, the entire volume of which the refractive index remains unchanged isCalled:optically homogeneous medium
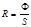 - formula for determining:luminosity
- formula for determining:luminosity
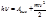 -formula:Einstein
-formula:Einstein
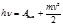 is expression:Einstein's formulas
is expression:Einstein's formulas
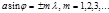 is:main minima in the diffraction of light by a diffraction grating
is:main minima in the diffraction of light by a diffraction grating
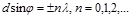 is:the main maxima of the diffraction of light on the diffraction grating
is:the main maxima of the diffraction of light on the diffraction grating
(в = 2,9 × 10-3 м × К ; s = 5,67 × 10-8 Вт /( м 2 × К 4 )): 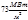
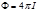 - formula for determining:the total luminous flux that emits a light source
- formula for determining:the total luminous flux that emits a light source 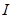
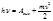 the expression is called:Einstein's formulas
the expression is called:Einstein's formulas
AAA
A constant diffraction grating is called:the total width of the slit and the opaque region between the slits
A light wave excited by a source can be represented as a result of a superpositionof coherent secondary waves emitted by fictitious sources. This is the formulationof the principle:Huygens-Fresnel
A necessary condition for interference of light is:coherence of waves
A normally parallel beam of monochromatic light with a wavelength l falls on a gap of width а =6 l . At what angle j will the third diffraction minimum of light be observed?:3 00
obtained imaginary?d less F
A normally parallel beam of monochromatic light 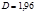 мм is incident on thediaphragm with a hole diameter
мм is incident on thediaphragm with a hole diameter 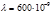 м). At what maximum distance
м). At what maximum distance 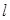 between the diaphragm and the screen in the center of the diffraction pattern,there will still be a dark spot?
between the diaphragm and the screen in the center of the diffraction pattern,there will still be a dark spot? 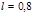 m
m
A one-dimensional diffraction grating is called:a system of parallel slots equal to the thickness lying in one plane and separatedby equal widths with opaque gaps
A phenomenon in which electrons are ejected by radiation from solid or liquid substances, while the substance itself is charged positively, is called:photoeffect
A phenomenon in which radiation is emitted from solid or liquid substances byelectrons, while the substance itself is charged positively:photoelectric effect
A plane passing through a vector 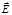 and a ray is called:plane of polarization
and a ray is called:plane of polarization
A plane passing through the focus perpendicular to the main optical axis is called:focal plane
A point on the main optical axis in which the refracted rays intersect converging rays incident on the lens parallel to the main optical axis is called:main focus
A ray of light comes out of turpentine into the air. The limiting angle of total internalreflection for this ray 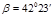 ..
..
A ray that has passed through a tourmaline crystal does not pass through another, perpendicular to the first. This is an example: polarization of light
A scientist who first measured speed by astronomical method:Remer
A straight line passing through the centers of the spherical surfaces of the lens iscalled:main optical axis
A strip colored in continuously alternating colors, with a light dispersion called:prismatic spectrum
Absolutely black body is called:body, completely absorbing all the energy that has fallen on it
Absolutely black body:body, completely absorbing all the energy that has fallen on it
Absorption of light is subject to law:Bouguer-Lambert
An electromagnetic light wave is called natural (unpolarized) if:directions of oscillations of vectors 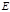 and
and 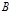 in this wave can lie in any planesperpendicular to the velocity vector of the wave propagationand the relative refractive index
in this wave can lie in any planesperpendicular to the velocity vector of the wave propagationand the relative refractive index
An optical set obtained from a microscope, if in it the lens and the eyepiece areInterchanged:telescopeAn optical device with which it is possible to spatially divide a beam of light into twoor more coherent beams and create a certain path difference between them is called:interferometer
Anisotropy is:dependence of physical properties of substances on the direction
As the wavelength increases, the refractive index of the medium increases. It:anomalous dispersion
At what angle between the planes of two nicols (the analyzer and the polarizer), theillumination on the screen, created by the light transmitted through them, decreasesby a factor of 4 compared to the illumination caused by light transmitted onlythrough the polarizer: 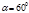
At what distance from a biconvex lens whose focal length is 40 cm, is it necessary to place an object so that its actual image is rendered in full size:80 cm
At what speed should an electron move so that its kinetic energy is equal to the energy of a photon with a wavelength of 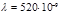 м?
м? 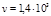 m/s
m/s
BBB
Brewster's law has the form: 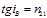
Brightness is:the ratio of the intensity of light within an elementary solid angle, resting on thearea to the area of the projection of this area on a plane perpendicular to thedirection of the ray
By the formula 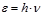 is defined:photon energy
is defined:photon energy
By the formula 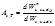 is defined:absorbance
is defined:absorbance
By the formula 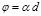 is defined:angle of rotation of the plane of polarization for optically active crystals and pureliquids
is defined:angle of rotation of the plane of polarization for optically active crystals and pureliquids
By the formula 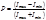 is defined:degree of polarization
is defined:degree of polarization
By the formula 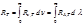 is defined:energy luminosity of the body
is defined:energy luminosity of the body
By the formula 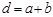 is defined:grating constant
is defined:grating constant
By the formula 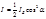 is defined:intensity of light transmitted through two polarizers
is defined:intensity of light transmitted through two polarizers
By the formula 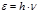 is defined:photon energy
is defined:photon energy
By the formula 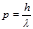 is defined:photon momentum
is defined:photon momentum
By the formula 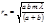 is defined:radius of the outer boundary of the
is defined:radius of the outer boundary of the 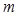 - Fresnel zone
- Fresnel zone
By the formula 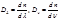 is defined:refractive index dispersion
is defined:refractive index dispersion
By the formula 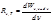 is defined:spectral density of energy luminosity
is defined:spectral density of energy luminosity
By the formula 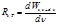 is defined:spectral density of energy luminosity
is defined:spectral density of energy luminosity
By the formula 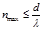 is defined:the maximum order of the spectrum given by the diffraction grating
is defined:the maximum order of the spectrum given by the diffraction grating
By the formula 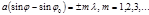 , the:diffraction minimum condition
, the:diffraction minimum condition
By the formula 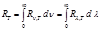 :energy luminosity of the body
:energy luminosity of the body
By the formula 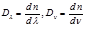 :refractive index dispersion
:refractive index dispersion
By what formula is the magnification of the telescope determined: 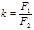
CCC
Calculate angle between the planes of two nicols (the analyzer and the polarizer), theillumination on the screen, created by the light transmitted through them, decreasesby a factor of 4 compared with the illumination caused by light transmitted onlythrough the polarizer: 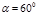
Choose Bouguer-Lambert law: 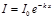
Choose the formula for photon momentum: 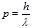
Choose the formula for the energy luminosity of a body: 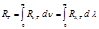
Coherent waves are:waves with the same frequency and unchanged phase difference
Compton effect is as follows:in the collision of quanta (photons) with free or almost free electrons, photons withlower energy are found in comparison with their energy before collision
Condition of the principal maxima for diffraction on a lattice: 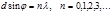
DDD
Designation of the light flux: 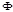
Devices for the acquisition, detection, analysis of polarized light, for research andmeasurements based on the phenomenon of polarization, are called:polarizers
Devices using induced radiation and operating in amplification and generation Mode:lasers, masers
Dichroism is:selective absorption of light as a function of the direction of oscillation of the lightwave 
Diffraction can be observed under the condition: 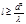
Diffraction grating:a set of a large number of obstacles and holes, concentrated in a confined space, onwhich diffraction of light occurs (glass plate)
Diffraction of light is:the phenomenon of the deviation of light from rectilinear propagation, when light,passing around an obstacle, enters the region of the geometric shadow
Double refraction is called:the ability of anisotropic substances to split an incident light beam into two beamspropagating in different directions with different phase velocities and polarized inmutually perpendicular directions
EEE
Each point to which the wave reaches reaches the source of the secondary waves,and the envelope of these waves gives the position of the wave front at the nextinstant of time. This is the formulation of the principle:Huygens
Electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths lie for the human eye in the rangefrom 400 to 760 nm:light
Enter the correct statement:light manifests itself both as an electromagnetic wave and as a stream of particles
Essence of the internal photoelectric effect is:under the influence of light incident on semiconductors and dielectrics, electrons are released from their atoms and become free
Expression 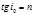 :Brewster's law
:Brewster's law
Expression 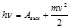 :Einstein's formula
:Einstein's formula
Films, on which the crystals of gerapatite-birefringent substance with pronounceddichroism in the visible region are applied, are called:polaroids
Expression 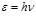 :Planck's formula
:Planck's formula
FFF
Find Bouguer-Lambert law: 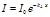
Find the angle of full polarization i Б when light is reflected from the glass, the refractive index of which is n= 1,57:i Б =57030 ¢
Find the correct statement for the phenomenon of light absorption:intensity of light as it passes through matter decreases exponentially
Find the correct statement:light manifests itself both as an electromagnetic wave and as a stream of particles
Find the focal length for a biconvex lens: 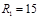 cm and
cm and 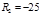 cm.:F=0,188 м
cm.:F=0,188 м
Find the linear dispersion D of the diffraction grating, the angular dispersion 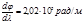 .. If the focal length of the lens projecting the spectrum onto the screen is F = 40cm:Д =81mcm/nm
.. If the focal length of the lens projecting the spectrum onto the screen is F = 40cm:Д =81mcm/nm
Find the momentum of a photon of red light rays ( 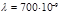 м):
м): 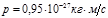
Find the radius of the fifth Fresnel zone, if the distance from the light source to thewave surface is a = 1m, the distance from the wave surface to the observation point isb = 1m:1,12 mm
Find the speed of light  in turpentine:2,02 × 108 м / с
in turpentine:2,02 × 108 м / с
Find the temperature  of the furnace if it is known that the radiation from thehole in it with an area of
of the furnace if it is known that the radiation from thehole in it with an area of 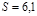 см2 has a power of
см2 has a power of 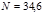 Вт.Radiation isconsidered close to the emission of an absolutely black body:T=1000 К
Вт.Radiation isconsidered close to the emission of an absolutely black body:T=1000 К
For anomalous dispersion is characteristic: 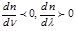
For dextrorotors, the condition: 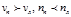
For left-handed substances, condition: 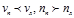
For monochromatic light, the Bouguer-Lambert law has the form: 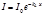
For normal dispersion is typical: 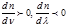
For the first time in 1845, the rotation of the plane of polarization in opticallyinactive substances was detected under the action of a magnetic field:Faraday
Formula 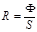 for:luminosity
for:luminosity
Formula determined the magnification of the telescope: 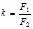
Formula 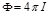 for:total luminous flux that emits a light source
for:total luminous flux that emits a light source 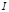
Formula for Illuminance: 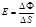
Full internal reflection occurs if ( 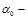 the maximum angle of total reflection,
the maximum angle of total reflection, 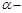 the angle of incidence):
the angle of incidence): 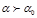
Full internal reflection occurs if ( 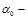 the maximum angle of total reflection,
the maximum angle of total reflection, 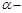 the angle of incidence):
the angle of incidence): 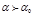
Full reflection condition: 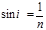
Give the correct statement for the theory of Fresnel zones:fluctuations of the reporting and odd Fresnel zones are in antiphase and, therefore,weaken each other
HHH
How called the absorption spectrum of isolated atoms:line spectrum
How called the distance from the center of the lens to the main focus:lens focal length
How is light pressure determined on a white surface? 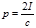
How many strokes 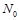 per unit length does the diffraction grating have if the green mercury line (
per unit length does the diffraction grating have if the green mercury line ( 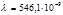 м) in the first-order spectrum is observed at an angle
м) in the first-order spectrum is observed at an angle 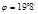 ?
? 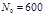 mm-1
mm-1
How mark in brightness: 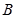
How mark in linear magnification: 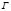
How name absorption of light:the phenomenon of a decrease in the energy of a light wave when it propagates
How name the spectral density of the energy luminosity:the energy emitted from a unit surface area of the body per unit time in thefrequency range of unit width
How name the molecular scattering:light scattering in pure media due to density, anisotropy, concentrationfluctuations
How name the index of refraction of the medium relative to the vacuum:absolute refractive index
Huygens-Fresnel principle is:the wave surface at any time is not just an envelope of secondary waves, but the result of their interference
How name light scattering:the process of the transformation of light by matter, accompanied by a change inthe direction of light propagation and the appearance of an improper glow ofmatter
III
Identification of brightness: 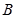
If light passes from optically denser medium 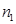 to medium optically less dense
to medium optically less dense 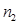 ,then the angle of refraction
,then the angle of refraction 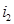 is greater than the angle of incidence
is greater than the angle of incidence 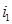 and viceversa. This is a consequence of the law:of refraction
and viceversa. This is a consequence of the law:of refraction
If the particle size of a cloudy medium is small compared to the wavelength oflight, then such a light scattering is called:the Tyndall effect
Illuminance is determined by the formula: 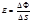
Illumination designation: 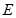
Illumination is:the ratio of the light flux to the surface
In an optically uniform transparent medium, light propagates along straight lines. This is the wording:law of rectilinear light propagation
In geometric optics, we consider:laws of light propagation in transparent media
In the courtyard at an altitude of 6 m are suspended two lamps of 500 cd each. Thedistance between the lamps is 8 m. Where is the more light on the Earth?in the center between the lamps
In the courtyard at an altitude of 6 m are suspended two lamps of 500 cd each. Thedistance between the lamps is 8 m. Where is the more light on the Earth?:in the center between the lamps
In the geometric optics, we consider, that:laws of light propagation in transparent media
Indicate enter an incorrect statement:the unit of illumination is 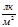
Indicate the correct statement for the phenomenon of light absorption:the intensity of light as it passes through matter decreases exponentially
Indicate the correct statement for the theory of Fresnel zones:fluctuations of the reporting and odd Fresnel zones are in antiphase and, therefore,weaken each other
Instruments using induced radiation and operating in the amplification and generation mode are called:lasers, masers
LLL
Law of illumination from a point source: 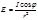
Law of Malus: 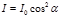
Lens equation: 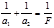
Light intensity designation: 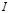
Light with an ordered direction of vibration of vectors 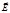 ,
, 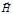 н, is called:polarized
н, is called:polarized
Light with all possible equiprobable directions of oscillations of a vector 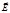 and
and 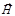 are called:unpolarized
are called:unpolarized
Light, directions of oscillations of vectors 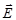 ,
, 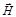 , which is predominant under theinfluence of external influences, is called:partially polarized
, which is predominant under theinfluence of external influences, is called:partially polarized
Light, directions of oscillations of vectors 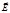 ,
,
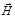
, which describe an ellipse lying ina plane perpendicular to the ray, is called:elliptically polarized
Light scattering is a process:the process of the transformation of light by matter, accompanied by a change inthe direction of light propagation and the appearance of an improper glow ofmatter
Light’s strength of a point source is determined by the formula: 
Lighting unit:suite
Linear magnification designation: 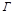
Luminosity designation is: 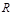
Luminosity is:the ratio of the total luminous flux emitted by the site in all possible directions, to
Luminous flux unit:lumen
MMM-NNN
Medium, the entire volume of which the refractive index remains unchanged isCalled:optically homogeneous medium
Molecular scattering is called:light scattering in pure media due to density, anisotropy, concentrationfluctuations
Monochromatic waves are waves:unbounded in space with a constant in time frequency, amplitude and initial phase
Name unit of measurement of the lens optical power:diopter
Name the distance between: lens focal length
OOO
Observe two phenomena: 1) a rainbow in the sky; 2) the decomposition of thewhite beam into seven colors of the rainbow after passing through the prism.These phenomena are explained:1 and 2-dispersion of light
Optical density of ice is less than water. In which of these environments does light propagate at a faster rate?on the ice
Optical power depends on:the refractive index of the lens and the radius of curvature of the spherical surfaces that bound the lens
PPP
Plank constant value: 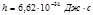
Point chapter of physics does optics belong:electrodynamics
Point Malus’s law: 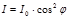
Point the Bouguer-Lambert law: 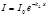
Point absorption of light is subject to law:Bouguer-Lambert
Point Brewster's Law: 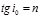
Point correct statement:light manifests itself both as an electromagnetic wave and as a stream of particles
Point distance between the main focus of the lens and the lens:lens focal length
Point formula for the spectral density of the energy luminosity: 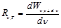
Point formula for dispersion of the refractive index: 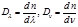
Point formula for photon energy: 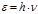
Point light flux: 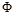
Point lighting unit:suite
Point luminous flux unit:lumen
Point the Bouguer-Lambert law: 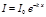
Point the condition of the principal maxima for diffraction on a lattice: 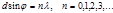
Point the condition of the principal maxima for oblique incidence of light on thediffraction grating: 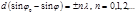
Point the correct statement:light manifests itself both as an electromagnetic wave and as a stream of particles
Point the definition for the absorption spectrum of a substance:the dependence of the monochromatic natural absorption coefficient on thewavelength
Point the definition for the polarization of light:a set of phenomena of wave optics, in which the transverse nature of
Point the formula for the angle of beam deflection by a prism: 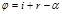
Point the formula to the strength of light from a point source: 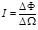
Point the full reflection condition: 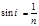
Point the Illumination designation: 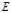
Point the light intensity: 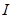
Point the main maxima of the diffraction of light on the diffraction grating areobserved under the condition: 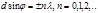
Point the maximum order of the spectrum given by the diffraction grating isdetermined by the formula: 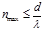
Point the principal minima in the diffraction of light by the diffraction grating areobserved under the condition: 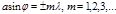
Point the unit of measurement of the optical force:diopter
Point the Rayleigh law: 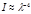
Point the value the Planck’s constant: 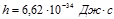
Point unit of measurement lens optical power :diopter
Point unit of measurement of illumination: 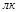
Point Wolf-Bragg’s formula: 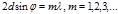
Problem. Two coherent monochromatic light sources are 1 mm apart and emit lightwith a wavelength of 0.5 мкм At what distance should a screen be placed from them,so that adjacent light interference strips are on it at a distance of 2 mm from eachother:4 m
RRR
Ratio of the angle of view obtained by the instrument to the angle of view underwhich the object is visible to the naked eye is called:an increase in the optical device
Red border of the photoelectric effect is the minimum frequency 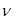 at which the external photoelectric effect begins
at which the external photoelectric effect begins
Relation between luminosity R and brightness B: 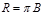
SSS
Scattering of light in pure media, caused by fluctuations in density, anisotropy,concentration, is called:molecular scattering
Selective absorption of light, depending on the direction of oscillation of the lightwave 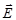 , is called:dichroism
, is called:dichroism
Set of phenomena of wave optics, in which the transverse nature ofelectromagnetic light waves is manifested:light polarization
Since light is of an electromagnetic nature, the application of this principle meansthat the resulting intensity of the electric and magnetic fields of two light wavespassing through one point is equal to the vector sum of the electric and magneticfield intensities of each of the waves separately. What is this principle?superposition principle
Show the lenses equation:: 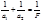
Solute problem. Radii of the curvature of the surfaces of a biconvex lens are given in 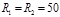 cm. Refractive index of the lens material
cm. Refractive index of the lens material 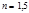 . Find the optical strength
. Find the optical strength  of the lens:D=2 diopter
of the lens:D=2 diopter
Specify the formula that defines the law of Malus: 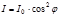
spectral density of its electrical luminosity is at a wavelength 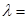 484nm?
484nm?
State the Huygens-Fresnel principle:a light wave excited by a source can be represented as the result of asuperposition of coherent secondary waves emitted by fictitious sources. This isthe formulation of the principle
Subject to observation 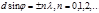 :the main maxima of the diffraction of light on the diffraction grating
:the main maxima of the diffraction of light on the diffraction grating
Subject to observation 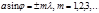 :main minima in the diffraction of light by a diffraction grating
:main minima in the diffraction of light by a diffraction grating
Substances that have the ability, in the absence of external influences, to rotate theplane of polarization are called:optically active
electromagnetic light waves
TTT
The 2 coherent monochromatic light sources are 1 mm apart and emit light with awavelength of 0.5 μm. At what distance should a screen be placed from them, so thatadjacent light interference strips are on it at a distance of 2 mm from each other:4 m
The ability of anisotropic substances to split an incident light beam into two rayspropagating in different directions with different phase velocities and polarized inmutually perpendicular directions is called:birefringence
The absoute refractive index shows:how many times the speed of light 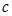 in a vacuum is greater than the speed of light
in a vacuum is greater than the speed of light 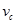 in a given medium
in a given medium
The absorption spectrum of isolated atoms is called:line spectrum
The absorption coefficient 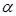 is:a dimensionless quantity equal to the ratio of the radiant energy absorbed by thisbody to the total radiant energy incident on it
is:a dimensionless quantity equal to the ratio of the radiant energy absorbed by thisbody to the total radiant energy incident on it
The absorption of light is called:the phenomenon of a decrease in the energy of a light wave when it propagates inmatter due to the transformation of wave energy into other types of energy
The absorption spectrum of dielectrics, the selective absorption of light in certain 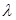 , when
, when 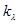 sharply increasing, is called:the continuous spectrum
sharply increasing, is called:the continuous spectrum
The absorption spectrum of a substance is:the dependence of the monochromatic natural absorption coefficient on thewavelength
The amplification of light (diffraction maxima) upon diffraction by a gap isdetermined by the condition: 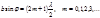
The angle 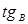 is called the angle:Brewster
is called the angle:Brewster
The angle of beam deflection by a prism: 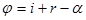
The angle of incidence of a ray of light on a mirror surface is 700. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the specular surface?200
The angle of rotation of the plane of polarization for optically active crystals andpure liquids is determined by the formula: 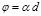
The application of a thin film to the surface of lenses and optical elements with arefractive index lower than the refractive index of glass is called:optical clarification
The area of the Fresnel 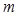 -zone is determined by the formula:
-zone is determined by the formula: 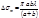
The attenuation of light (diffraction minima) upon diffraction by a gap is determinedby the condition: 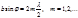
The Bouguer-Lambert law has the form: 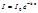
The Brewster's Law: 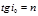
The brightness is determined by the formula: 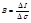
The candela is a unit of measurement:powers of light
The candela is a unit of:powers of light
The candela is a unit that use for measure:powers of light
The chemical effect of light is manifested in:photosynthesis
The phenomenon used in photosynthesis:chemical action of light
The coherent waves are:waves with the same frequency and unchanged phase difference
The collecting lens, whose optical power in the air is 8 dp, in some liquid acts as ascattering lens with a focus of F = -1m. The refractive index of the lens glass is 1.5.Determine the refractive index of a liquid:1,6
The Compton Effect:in the collision of quanta (photons) with free or almost free electrons, photons withlower energy are found in comparison with their energy before collision
The concentric rings observed with interference of light from an air gap formed by aplane-parallel plate and a plane-convex lens with a large radius of curvature in contact with it are called:Newton's rings
The enlightenment of optics is called:the application to the surface of lenses and optical elements of a thin film with a refractive index lower than the refractive index of the glass
The condition 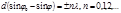 is:main maxima for inclined light incidence on the diffraction grating
is:main maxima for inclined light incidence on the diffraction grating
The condition of maxima in the interference of light: 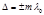
The condition of minima with interference of light: 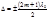
The condition of the principal maxima for oblique incidence of light on thediffraction grating: 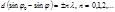
The constant of the diffraction grating is d=2,5 мкм. Find the angular dispersion of the lattice for 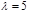 ,
, 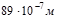 in the first-order spectrum:4,1 × 105 рад / м
in the first-order spectrum:4,1 × 105 рад / м
The constant of the diffraction grating is determined by the formula: 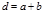
The degree of polarization depends on:angle of incidence of natural light on the interface between isotropic dielectrics
The degree of polarization is denoted by: 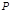
The degree of polarization is determined by the formula: 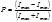
The dependence of the intensity distribution on the screen on the diffraction angleis called:diffraction spectrum
The dependence of the monochromatic natural absorption index on the wavelength is called:the absorption spectrum of the substance
The dependence of the physical properties of substances on the direction is called:anisotropy
The dependence of the refractive index of a substance on the wavelength of light is Called:dispersion of light
The dependence of the phase velocity of light in the medium on the frequency oflight is called:dispersion of light
The variance of light is:dependence of the phase velocity of light in the medium on the frequency of light
The diffraction minimum condition: 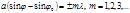
The diffraction spectrum is called:the dependence of the intensity distribution on the screen on the diffraction angle
The dispersion of the refractive index is determined by the formula: 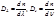
The distance between the main focus of the lens and the lens is called:lens focal length
The distance from the center of the lens to the main focus is called:lens focal length
The energy luminosity of a body is determined by the formula: